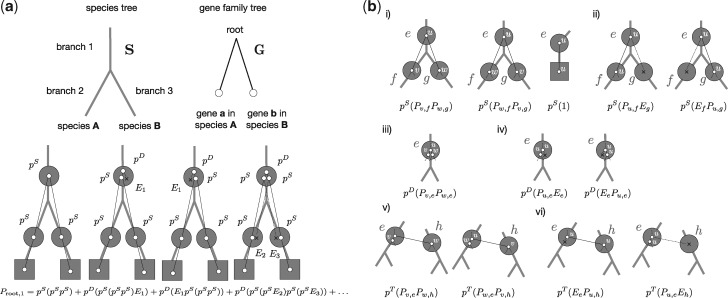
Fig. 2.
Calculating the probability of G along S. (a) The probability that the rooted GFT G is generated along the rooted species tree S according to the “undated” DTL process can be calculated by summing over all reconciliations. Here, we show the leading terms in the sum over all reconciliations that start with a single gene copy on branch 1 of S and obtain a rooted gene tree that is congruent with G. (b) More generally, to calculate , that is, the sum over all reconciliations generating the subtree below some internal node u of G starting from a single gene present on the internal branch e of S, we must consider the following events (i) if e is an internal branch of S, speciation with probability pS such that the descendants of v on G are observed on f of S and of w on G are observed on g of S, or vice versa. If e is a terminal branch, with probability pS gene u will be observed at the terminal branch e; (ii) if e is an internal branch of S, speciation with probability pS such that the descendants of u are observed on f of S and the copy on g goes extinct with probability Eg, or vice versa; (iii) duplication with probability pD such that v and w are both observed on e; (iv) duplication with probability pD such that either the first or the second copy goes extinct, each with probability Ee and u is observed on e; (v) transfer with probability pT, such that the respective branches v and w correspond to the copy on the donor branch e of S, whereas the other copy corresponds to the recipient copy on branch h of S that is not an ancestor of e; and finally (vi) transfer with probability pT followed by the extinction of either, the copy in the donor linage e with probability Ee of the extinction of the copy in the recipient, with probability Eh. These correspond to the terms of equation (2).