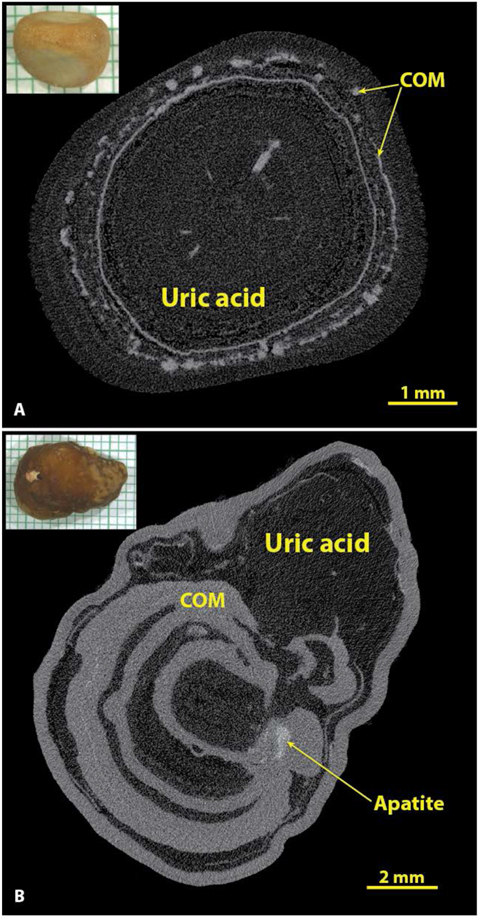
Figure 7.
Uric acid in stones has the lowest X-ray attenuation values of the common stone minerals. A: A typical uric acid stone, nearly pure (93% uric acid by volume). B: A stone with alternating layers of uric acid and COM. In both A and B the uric acid was of the anhydrous form by spectroscopic analysis, but the dihydrate form of uric acid looks exactly the same by micro CT.