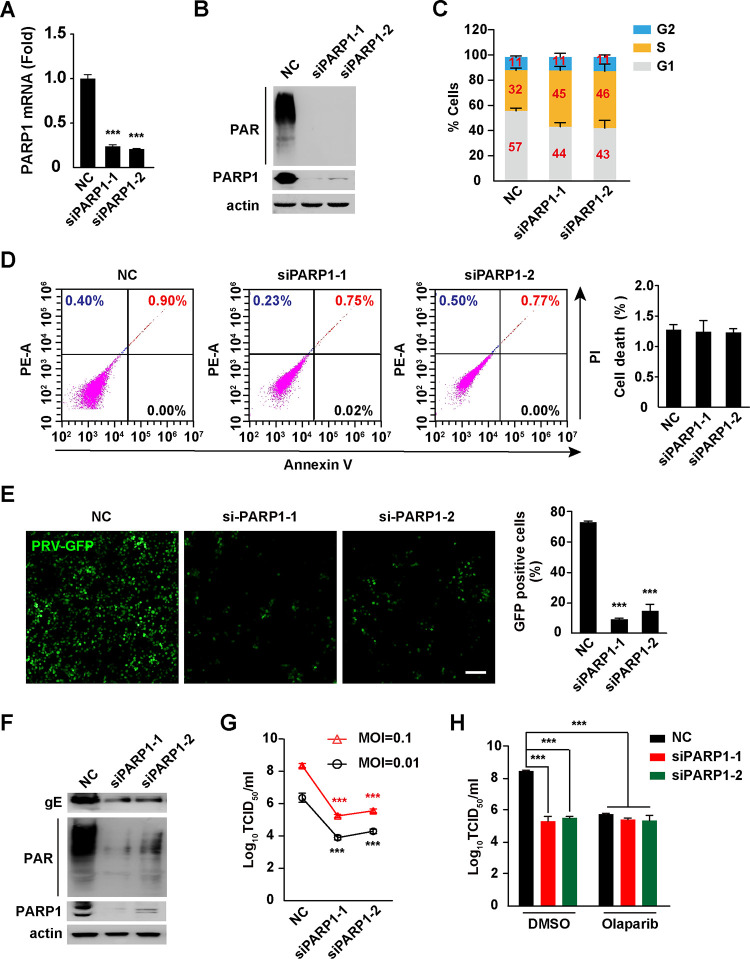
FIG 3.
Knockdown of PARP1 inhibits PRV infection. (A) PK15 cells were transfected with NC, siPARP1-1, and siPARP1-2 for 48 h. The PARP1 mRNA level was assessed by qRT-PCR analysis. (B) PK15 cells were transfected with NC, siPARP1-1, and siPARP1-2 for 48 h. PAR, PARP1, and actin were assessed by immunoblotting analysis. (C) PK15 cells were transfected with NC, siPARP1-1, and siPARP1-2 for 48 h. The cell cycle was assessed with Hoechst 33342 staining in flow cytometry. (D) PK15 cells were transfected with NC, siPARP1-1, and siPARP1-2 for 48 h. Apoptosis was assessed with annexin V-FITC and PI staining in flow cytometry (left). Quantification of the percentage of cell death is shown on the right. (E) PK15 cells were transfected with NC, siPARP1-1, and siPARP1-2 for 24 h and infected with PRV-GFP (MOI = 0.01) for 36 h. Viral replication was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy (left), and GFP-positive cells were analyzed by flow cytometry (right). Bar, 100 μm. (F) PK15 cells were transfected with NC, siPARP1-1, and siPARP1-2 for 24 h and infected with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1) for 24 h. PRV gE, PAR, PARP1, and actin were assessed by immunoblotting analysis. (G) PK15 cells were transfected with NC, siPARP1-1, and siPARP1-2 for 24 h and infected with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.01 and 0.1) for 24. PRV titers were assessed by TCID50 assay. (H) PK15 cells were transfected with NC, siPARP1-1, and siPARP1-2 for 24 h. Cells were infected with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.01 and 0.1) and simultaneously treated with DMSO or olaparib (10 μM) for 24 h. PRV titers were assessed by TCID50 assay. Data are means and SD based on three independent experiments. ***, P < 0.001, determined by two-tailed Student's t test (A, E, and G) or one-way ANOVA (H).