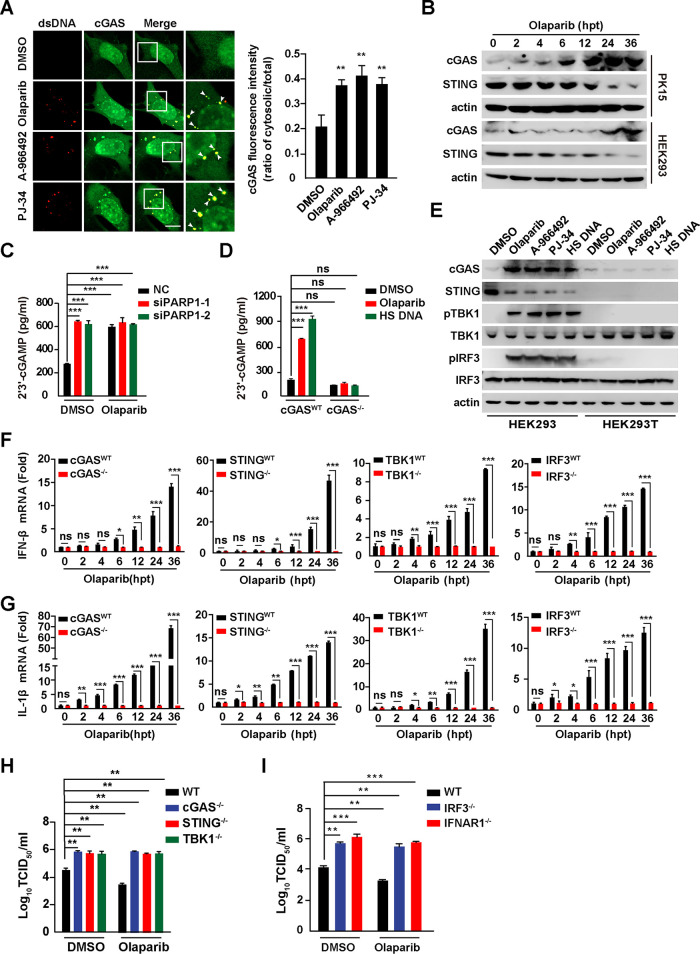
FIG 6.
Inhibition of PARP1 activates cGAS-STING pathway. (A) PK15 cells were treated with DMSO, olaparib (10 μM), A-966492 (30 nM) or PJ-34 (30 nM) for 24 h. cGAS and dsDNA were detected by immunofluorescence. Colocalization of cGAS with dsDNA is indicated by arrowheads (left). (Right) Quantification of the ratio of cytosolic versus total cGAS. Bar, 10 μm. (B) PK15 and HEK293 cells were treated with olaparib (10 μM) for 0 to 36 h. cGAS, STING, and actin were assessed by immunoblotting analysis. (C) PK15 cells were transfected with NC, siPARP1-1, and siPARP1-2 and simultaneously treated with DMSO or olaparib (10 μM) for 48 h. 2′,3′-cGAMP in the cells was assessed by ELISA. (D) WT and cGAS−/− PK15 cells were treated with DMSO or olaparib (10 μM) or transfected with HT DNA (0.3 μg) for 24 h. 2′,3′-cGAMP in the cells was assessed by ELISA. (E) HEK293 and HEK293T cells were treated with DMSO, olaparib (10 μM), A-966492 (30 nM), or PJ-34 (30 nM) or transfected with HT DNA (0.3 μg) for 24 h. cGAS, STING, p-TBK1, TBK1, p-IRF3, IRF3, and actin were assessed by immunoblotting. (F and G) WT, cGAS−/−, STING−/−, TBK1−/−, and IRF3−/− PK15 cells were treated with olaparib (10 μM) for 0 to 36 h. IFN-β (F) and IL-1β (G) mRNA levels were assessed by qRT-PCR analysis. (H) WT, cGAS−/−, STING−/−, and TBK1−/− PK15 cells were infected with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1) and simultaneously treated with DMSO or olaparib (10 μM) for 24 h. PRV titer was assessed by TCID50 assay. (I) WT, IFR3−/−, and IFNAR1−/− PK15 cells were infected with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1) and simultaneously treated with DMSO or olaparib (10 μM) for 24 h. PRV titer was assessed by TCID50 assay. Data are means and SD from three independent experiments. ns, no significance. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01, and ***, P < 0.001, determined by two-tailed Student's t test. hpt, hours posttreatment.