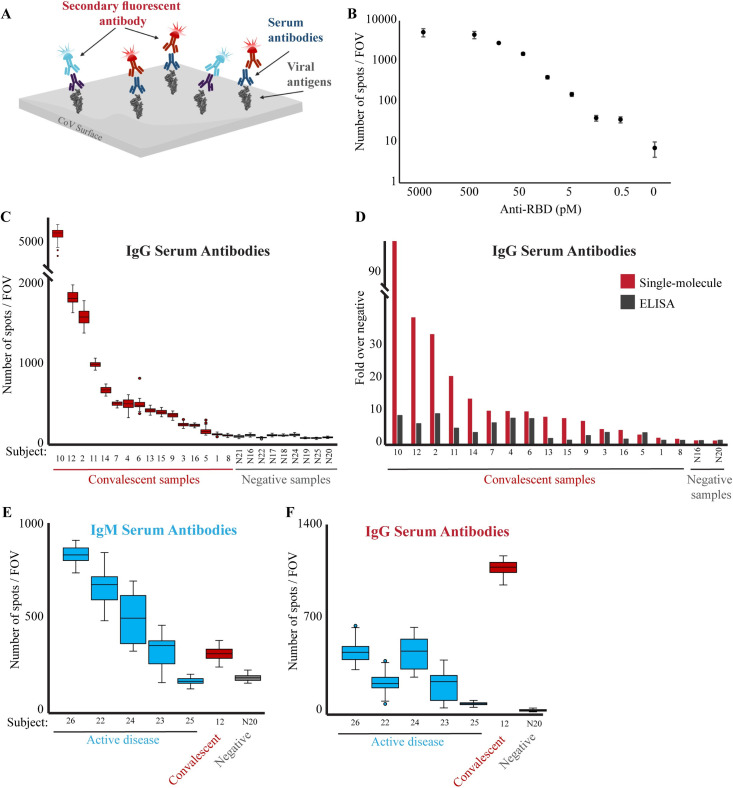
Fig 2. Single-molecule detection of anti-RBD antibodies.
(A) Scheme of the serological diagnostic test. Serum samples are incubated with biotin-conjugated viral antigen (RBD) and loaded on a PEG-coated, streptavidin activated coverslip. Multiplex of fluorescently-labeled anti-human IgG (red) and IgM (light blue) antibodies are added to the flow cell and imaged. (B) Human anti-RBD antibodies at the indicated concentrations were incubated with biotin-RBD, and detected by fluorescently-labeled anti-human IgG antibodies. The Antibodies LoD is at picomolar concentrations. Both axes are in logarithmic scale, and the no anti-RBD antibody data point is not to scale. (C) Serum samples from either convalescent or not-infected subjects were diluted 1:2500 and analyzed as described in B to detect the presence of anti-RBD IgG antibodies in the subjects’ serum. The box plot shows the number of spots per FOV for all the FOV imaged for each sample in this experiment. Group statistics: all negative samples: mean 63.1, CV 0.3; all positive samples: mean 827.3, CV 1.5. Median values of each group were compared by t-test, p-value < 0.05. (D) Comparison between single-molecule and ELISA detection of anti-RBD antibodies. Single-molecule imaging and ELISA against anti-RBD antibodies were conducted on the same samples. Signals from each assay were normalized compared to the negative serum samples. Single-molecule imaging provides greater sensitivity and dynamic range in detecting anti-RBD antibodies in serum. (E, F) Serum from subjects with an active COVID-19 disease (blue), convalescent (red), or not-infected (gray) subjects, were diluted 1:2500, incubated with biotin-RBD and loaded on a streptavidin-coated surface. Fluorescently labeled anti-human IgM (E) or IgG (F) antibodies were imaged and quantified.