FIGURE 3.
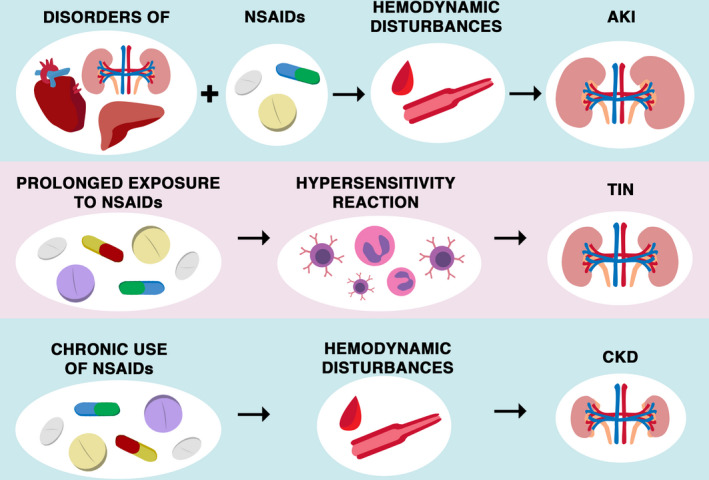
Summarization of main renal pathomechanisms associated with NSAIDs usage. The usage of NSAIDs could disturb kidney function in multiple pathways. The chronic usage of NSAIDs could lead to CKD as the effect of hemodynamic disturbances. The TIN could be the effect of the consequence of prolonged exposure to NSAIDs. A possible mechanism is assigned to a delayed hypersensitivity reaction, with interstitial infiltration of eosinophils and T cells. NSAIDs could also lead to AKI, especially in patients with comorbidities and polypragmasia. AKI, acute kidney injury; CKD, chronic kidney disease; NSAID, nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs; TIN, tubulointerstitial nephritis
