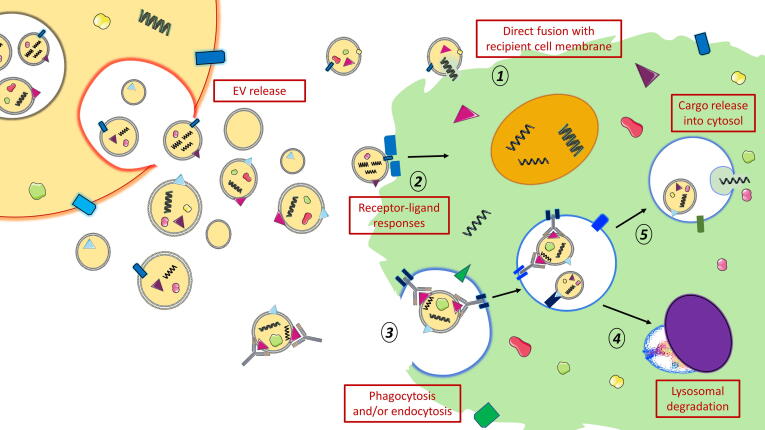
Fig. 3.
Proposed methods of exosome uptake. Exosomes can generate numerous responses in recipient cells, and are suggested to do so through at least three different mechanisms. Exosomes and other vesicles might directly fuse to the plasma membrane of the recipient cell, although the biological pathways involved in this are still poorly understood (1). Exosomes might also directly target receptors on the exterior surface of the recipient cell, driving host responses e.g. by co-stimulation through receptor-ligand interactions (2). Exosomes are also known to be taken up by recipient cells by phagocytosis, macro/micropinocytosis or endocytosis (caveolin/clathrin-dependent, receptor or antibody-mediated) (3). From our studies, we showed that antibodies enhance uptake of extracellular vesicles (EVs) into recipient cells, which are subsequently targeted for lysosomal degradation (4). Alternatively, internalised exosomes and other vesicles might utilise endosomal escape to release their contents directly or indirectly into the recipient cell cytosol (5). Images are adapted from Servier Medical Art by Servier (http://smart.servier.com/) and modified by the authors under the following terms: Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported (CC BY 3.0).