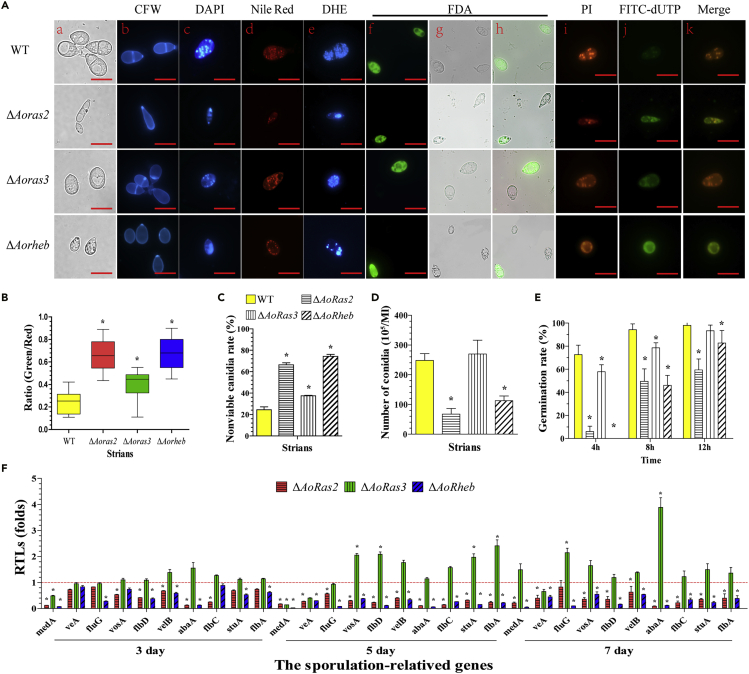
Figure 2.
Comparison of conidiation, conidial germination, conidial activity, DNA fragmentation, and cell apoptosis between WT and mutant strains of A. oligospora
(A) Conidia of WT and mutant strains were stained with CFW, DAPI, Nile Red, DHE, and FDA, followed by the TUNEL analysis. a. Conidia morphology of WT and mutant strains was observed under a light microscope. Conidia were stained with (b) CFW, (c) DAPI, (d) Nile Red, (e) DHE, and (f–h) FDA. The viable conidia stained with FDA emitted bright green fluorescence, whereas the nonviable ones did not show this effect. i–k. TUNEL analysis of spores. Samples were examined under a confocal laser scanning microscope. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(B) Analysis of DNA fragmentation and cell apoptosis in the conidia. The ratio of green to red fluorescence intensity was determined for at least 30 fields viewed under a microscope, and the horizontal bars depict the median. The asterisk indicates a significant difference between the mutants and the WT strain (Tukey's HSD, p < 0.05).
(C) Percentages of nonviable conidia of the WT and mutant strains.
(D) Comparison of conidial yields between the WT and mutant strains.
(E) Conidial germination rates in WT and mutant strains.
(F) Relative transcription levels (RTLs) of sporulation-related genes in the mutant strain compared with those of the WT strain at different time points. The red line indicates the standard (which has an RTL of 1) for statistical analysis of the RTL of each gene in a deletion mutant compared with that in the WT strain under a given condition. Error bars in (C–F): Data are represented as mean ± SD. The asterisk in (C–F) indicates a significant difference between mutants and the WT strain (n = 3 for the WT strain (C–E), n = 9 for each mutant strain (C–E), n = 3 for each gene (F); Tukey's HSD, p < 0.05).