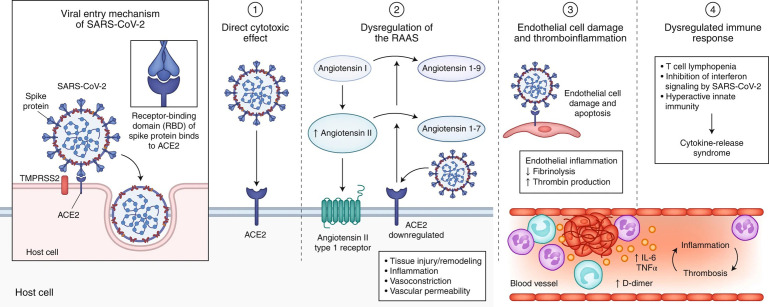
Fig. 1.
SARS-CoV-2 enters host cells through interaction of its spike protein with the entry receptor ACE2 in the presence of TMPRSS2 (far left). Proposed mechanisms for COVID-19 caused by infection with SARS-CoV-2 include (1) direct virus-mediated cell damage; (2) dysregulation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) as a consequence of downregulation of ACE2 related to viral entry, which leads to decreased cleavage of angiotensin I and angiotensin II; (3) endothelial cell damage and thromboinflammation; and (4) dysregulation of the immune response and hyperinflammation caused by inhibition of interferon signaling by the virus, T-cell lymphodepletion, and the production of proinflammatory cytokines, particularly IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α.
(From Gupta A, Madhavan MV, et al. Extrapulmonary Manifestations of COVID-19. Nat Med. 2020; 26: 1017-2032, with permission.)