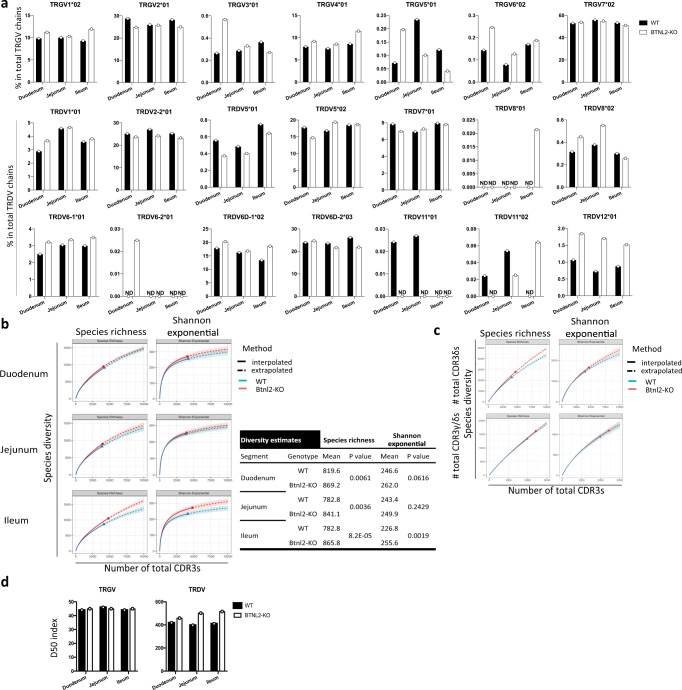
Fig. 5. Ileal Btnl2-KO γδ IELs exhibit more diverse TRGV repertoire compared to ileal WT γδ IELs.
γδ IELs from the duodenum, jejunum, and the ileum of cohoused 11-week-old Btnl2-KO and WT littermates (n = 3–4/genotype, a pool of 2 mice, each) were sort-purified as CD45 + TCRβ-TCRγδ + cells. Two-thirds of each sample were processed for deep bulk RNA sequencing and one-third of each sample was pooled per genotype per segment and used for single-cell sorting and single-cell TCR sequencing. γδ IELs from duodenum, jejunum, and ileum of cohoused 11-week-old Btnl2-KO and WT littermates (n = 8 mice, each) were single-cell sorted and single-cell TCR sequencing analysis of TCR Vγ and TCR Vδ chain usage and CDR3 aminoacid sequences was performed. a TRGV*J and TRDV*J gene usage in Btnl2-KO and WT γδ IELs. ND not detected. b Top-Diversity estimates for TRG only CDR3 aminoacid sequences in Btnl2-KO and WT γδ IELs. Shaded areas indicate the 95% confidence interval by 50 bootstrap replicates. Bottom-TRG diversity estimates at interpolation point 3500, where p value is derived from t-test based on 50 bootstrap replicates. c Diversity estimates for TRD only and paired TRG and TRD CDR3 aminoacid sequences, respectively, in ileal Btnl2-KO and WT γδ IELs. Shaded areas indicate the 95% confidence interval by 50 bootstrap replicates. d Diversity 50 (D50) index represented as the number of top unique clones that comprise 50% of the TRGV and TRDV repertoires, respectively, normalized to the total number of unique clones of duodenal, jejunal and ileal Btnl2-KO and WT γδ IELs.