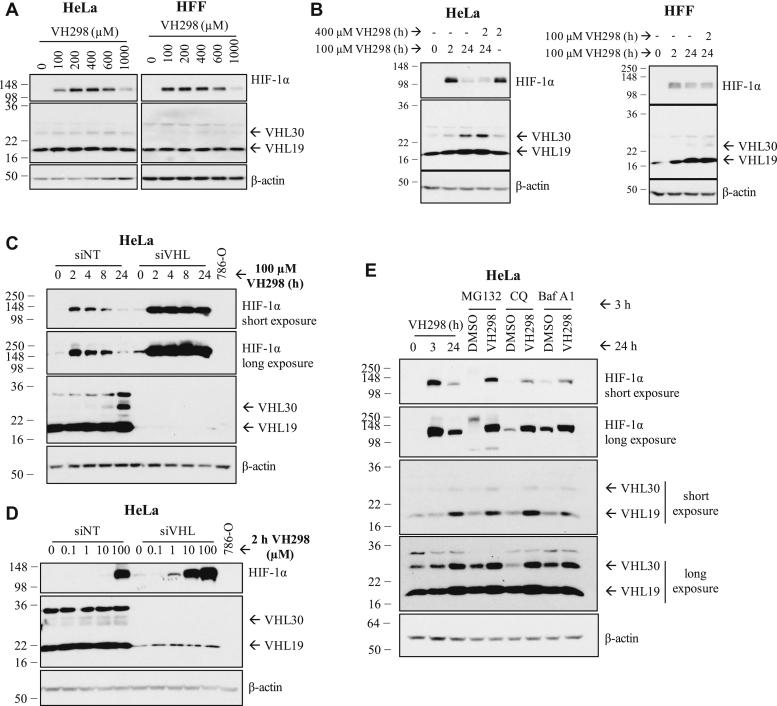
Figure 4.
The decrease of HIF-1α protein levels in prolonged VH298 treatment is mediated by proteasomal degradation in a VHL-dependent manner.A, dose-dependent immunoblots of HIF-1α in HeLa (left panel) and HFF (right panel) cells treated with VH298 for 2 h. B, HeLa and HFF cells were treated with 100 μM of VH298 for 2 and 24 h. After 24 h treatment of 100 μM VH298, 400 μM of VH298 was introduced to HeLa cells for 2 h and 100 μM of VH298 to HFF cells for 2 h. A 2 h treatment with 400 μM of VH298 was also included in HeLa cells. C and D, HeLa cells were transfected with nontargeting siRNA control (siNT) or VHL siRNA (siVHL). C, after 24 h, media were changed, and transfected cells were treated with 100 μM of VH298 for indicated times. D, after 46 h, media were changed, and transfected cells were treated with indicated concentrations of VH298 for 2 h. Cell lysate of 786-O was included as negative control for VHL. E, HeLa cells were treated with 3 and 24 h of 100 μM VH298. After 24 h treatments of 0.5% DMSO or 100 μM VH298, cells were treated with proteasome inhibitor MG132 (20 μM), autophagy inhibitors chloroquine (CQ; 50 μM) or bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1; 50 nM) for 3 h. Protein levels were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against HIF-1α, VHL, and β-actin, which acted as a loading control. The blots shown are representative of three independent experiments. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; HFF, human foreskin fibroblast; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α.