Figure 7: Inhibition of the MPTP and replenishment of NAD+ leads to cardiomyocyte protection after IAV infection.
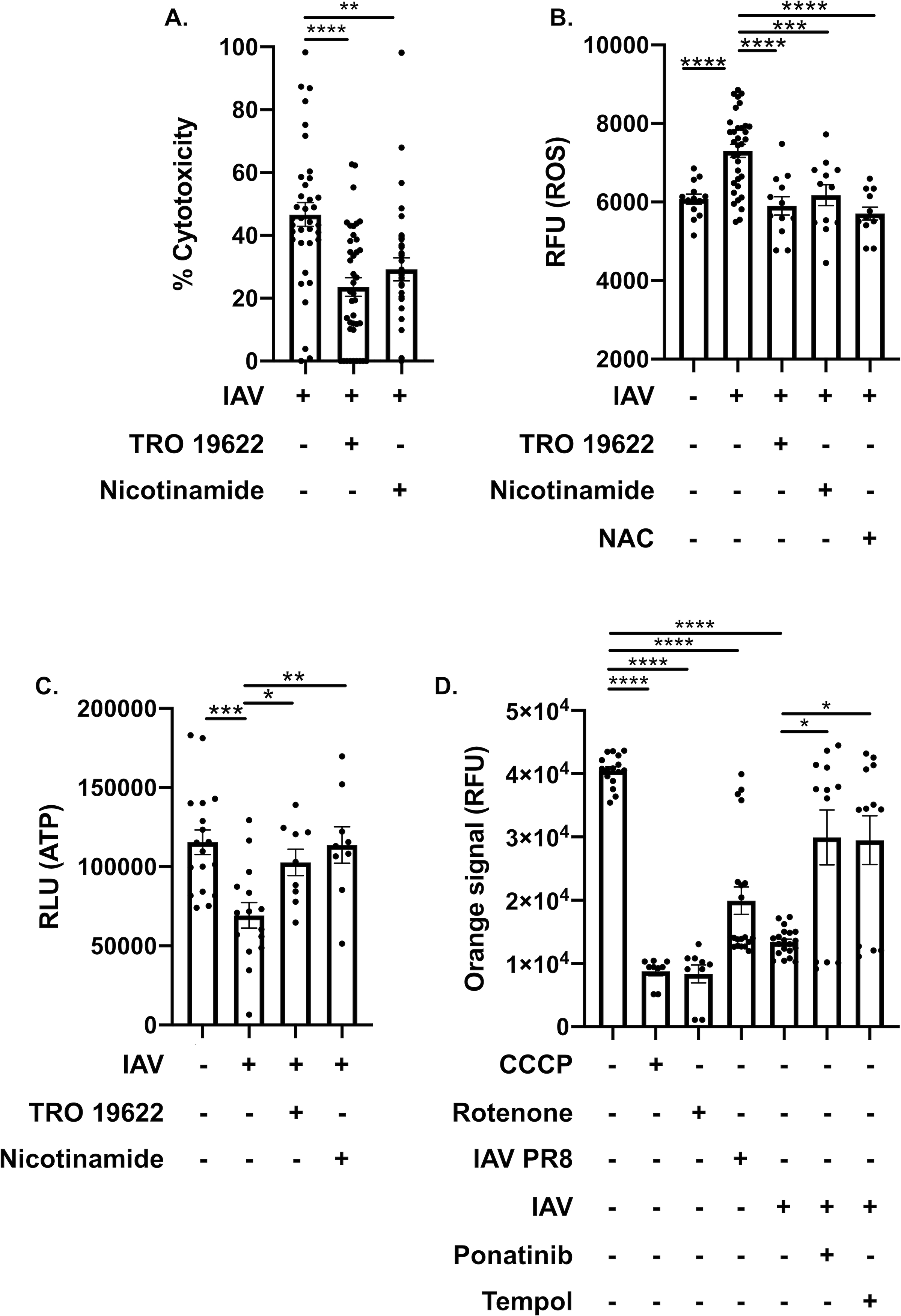
(A) Cytotoxicity of H9c2 myocytes treated with TRO 19622 (10 μM) or nicotinamide (1 mM) infected with A/California/7/2009 (IAV). (B) ROS/superoxide levels and (C) ATP levels of IAV-infected H9c2 myocytes treated with TRO 19622, nicotinamide with same concentration in (A) or n-acetylcysteine (10 μM), compared to uninfected or mock treated H9c2. RLU: relative light unit of luminescence. (D) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization assay as measured via changes in RFU: relative fluorescent units of human AC16 cardiomyocytes infected with A/California/7/2009 (IAV) or PR8 and treated with rotenone, tempol or ponatinib. Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone (CCCP) positive control for mitochondrial membrane permeabilization. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple-comparison post-test. Asterisks denote the level of significance observed: * = p ≤ 0.05; ** = p ≤ 0.01; *** = p ≤ 0.001, **** = p ≤ 0.0001.
