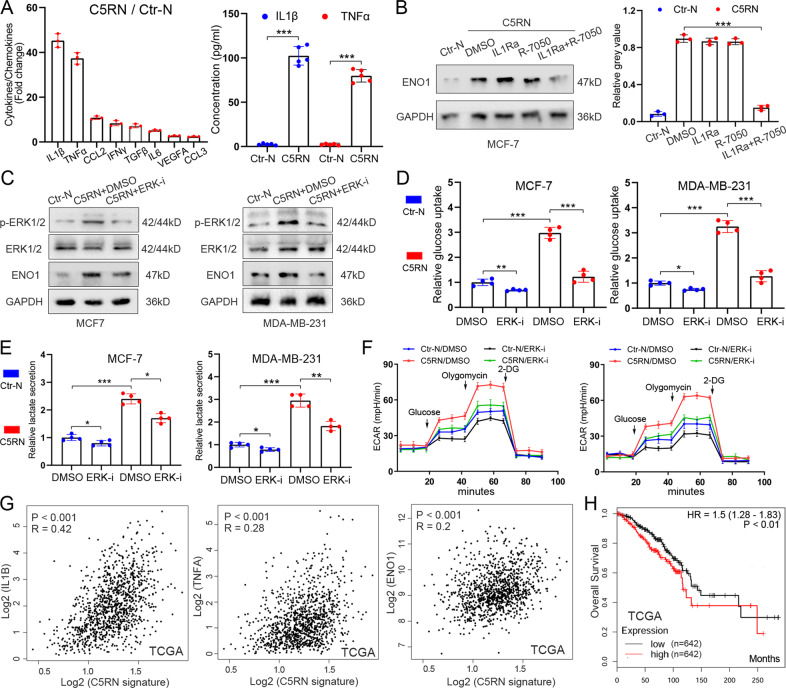
Fig. 4. ERK1/2-ENO1 signaling is essential to C5aR1+ neutrophil-induced breast cancer cell glycolysis.
A PCR array revealing a panel of significantly changed cytokine/chemokine mRNAs in C5aR1+ neutrophils (C5RN) relative to C5aR1-negative neutrophils (Ctr-N) (left). ELISA showing the expression of IL1β and TNFα in C5RN and Ctr-N (right). B Synergetic inhibition of IL1R and TNFR markedly abolished C5RN-induced ENO1 upregulation in BC cells. C Immunoblotting analysis of p-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), ERK1/2, and ENO1 in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells with C5RN or C5RN plus ERK1/2 suppression (SCH772984). D Glucose uptake was determined in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells with C5RN or C5RN plus ERK1/2 inhibition (SCH772984). E Lactate production was examined in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells with C5RN or C5RN plus ERK1/2 inhibition (SCH772984). F Analysis of ECAR in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells with C5RN or C5RN plus ERK1/2 inhibition (SCH772984). G Scatter plot analysis revealing levels of L1β, TNFα, ENO1, and C5RN gene signature correlated in BC tissues. H Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showing overall survival based on the expression of C5RN gene signature and ENO1 in TCGA. Data represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.