Figure 6.
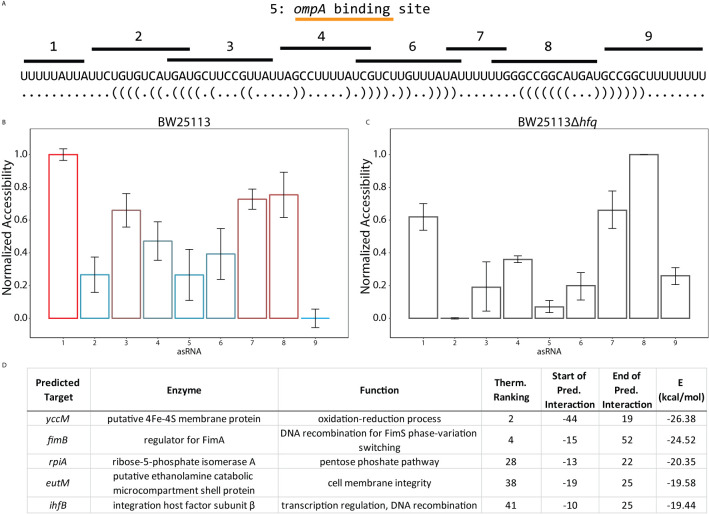
Target predictions informed by accessibility profiles suggest global post-transcriptional activity of RseX. (A) In vivo accessibility profile of RseX previously determined using a high throughput regional RNA accessibility quantification assay termed INTERFACE (Mihailovic et al., 2018). Targeted regions are indicated above the accepted RseX sequence. The region targeted by asRNA 5 corresponds to the predicted ompA binding site (Guillier et al., 2006). (B) RseX accessibility in WT E. coli BW25113 as collected in (Mihailovic et al., 2018). Results are normalized from 0 to 1 to allow for comparison across conditions (i.e., varying abundance). Colors correspond to traditional visual representation of in vivo accessibility data (red = highly accessible, blue = lowly accessible). Error bars represent standard error of the mean. (C) RseX normalized accessibility in a kanR-cured isogenic Δhfq strain (Baba et al., 2006). Likely-functional region 1 decreases accessibility (p-value < 0.05 2-tailed Student’s t-test) in the absence of match-maker Hfq, unlike likely-functional region 8. (D) Top-5 filtered target predictions of RseX at functional region 1. Two predicted targets, ihfB and fimB, were identified as most interesting given the newly confirmed global silencer (H-NS) of RseX, as both mRNAs encode for accepted transcriptional regulators. Start and end coordinates of putative RseX binding are listed for each mRNA with respect to translational start.