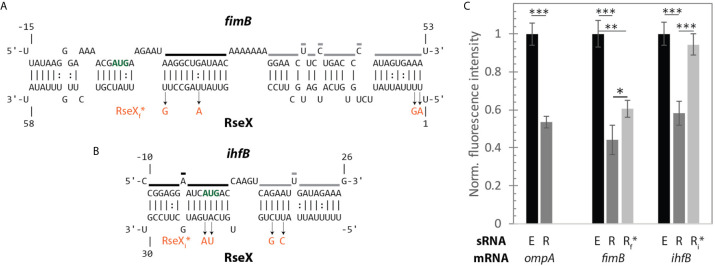
Figure 9.
A fluorescent reporter system confirms direct translational regulation of mRNAs fimB and ihfB by RseX in vivo. (A) IntaRNA-predicted interaction between RseX and fimB. Start codon is outlined in bold green font; regions that are strongly (black) and weakly (grey) protected from cleavage in the presence of RseX, as determined by PbAc probing, are traced. RseX sequence mutations used in reporter assays, designed to limit changes in predicted structure, are listed in orange. (B) IntaRNA-predicted interaction between RseX and ihfB. Start codon, in vitro RseX-protected regions, and point mutations are outlined as in panel (A). (C) gfp assays elucidate repressive in vivo effects of RseX on previously-confirmed (ompA) and novel (fimB, ihfB) targets at OD600 1. ΔrseX strains harboring pNM12 (black), pBAD-RseX (dark grey) or pBAD-RseX mutant (light grey, RseXf* or RseXi* for fimB and ihfB, respectively) were induced by addition of 0.05% arabinose at OD600 ~ 0.15; respective pLacO-ompA/fimB/ihfB-gfp constructs were simultaneously induced with 1 mM IPTG. Illustrated means represent median fluorescence as normalized to respective pNM12 controls; samples for each median were collected in at least triplicate. Error bars represent propagated standard deviation of the mean and asterisks indicate significant differences as evaluated by unpaired Student’s t-test (p-value < 0.001, < 0.01, < 0.05 are represented as ***, **, and *, respectively). Positive control ompA as well as novel targets fimB and ihfB are repressed upon RseX expression, as compared to an empty control (p-value < 0.001). Repression of fimB by RseX is alleviated partially by 4 point mutations in RseX (RseXf*) outlined in (A) (p-value < 0.05). Repression of ihfB by RseX is fully abolished by 4 point mutations in RseX (RseXi*) (p-value < 0.001).