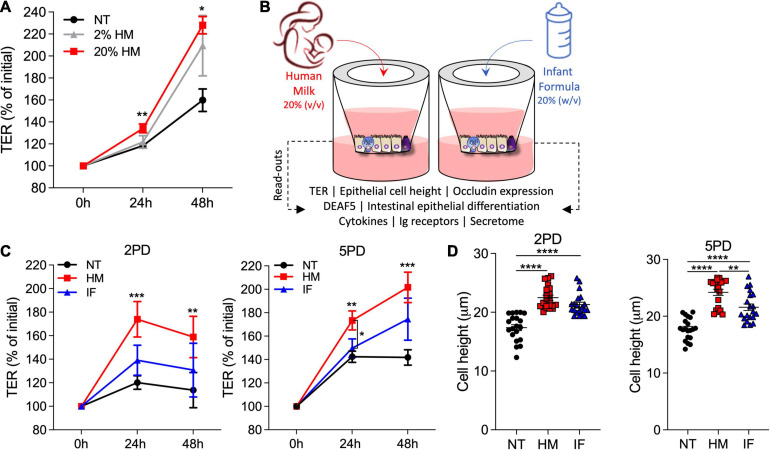
FIGURE 2.
Human milk decreases ion permeability of the pediatric intestinal epithelium. (A) TER values of 2PD monolayers apically exposed to human milk (HM) 2 or 20% (v/v). (B) Schematic representation of pediatric HIE treatment and biological readouts. (C) TER measurement of 2PD and 5PD monolayers apically treated with 20% (v/v) of HM or 20% (w/v) of commercial infant formula (IF). (A,C) Mean ± SEM are shown. Data are representative of three independent experiments with n = 3–6 enteroid monolayers/group per experiment. p-values were calculated by Mann Whitney test. Unless indicated, p-values correspond to treated vs. non-treated (NT) controls. (D) Epithelial cell height quantified by immunofluorescent microscopy (≥10 different view fields). Data represent mean ± SEM of three combined experiments, each including four monolayers/group per experiment. Each symbol indicates an independent monolayer. p-values were calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc analysis. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.