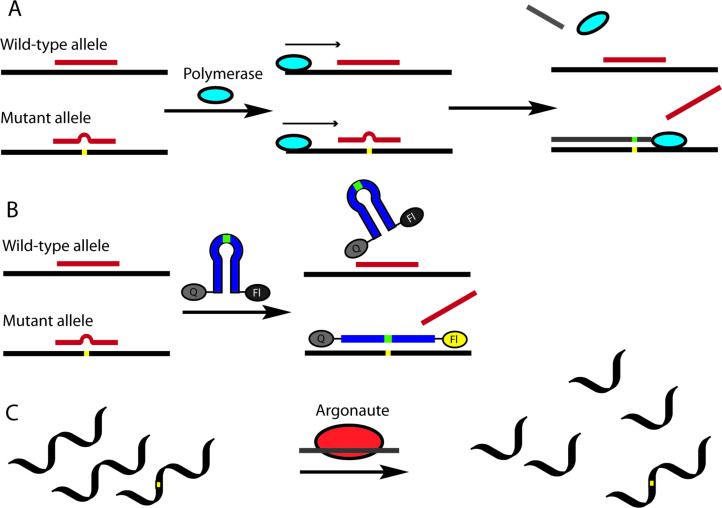
Figure 21.
PNA clamp (red) binding to target DNA containing a mixture of sequences (A) PNA binds with higher affinity to the perfectly matched wild-type sequence while binding to the mutant containing as few as one mismatch is weaker. Once elongation begins, the perfectly matched complex stalls the polymerase inhibiting elongation while the mismatched complex dissociates allowing for elongation to continue; (B) LNA probes (blue) can also out compete PNA/DNA complexes mismatched allowing for sequence selective detection of mutant alleles; (C) NAVIGATER uses DNA-guided Argonaute to selective degrade wild-type oligos to enrich the mutant population increasing the sensitivity of PCR clamping.