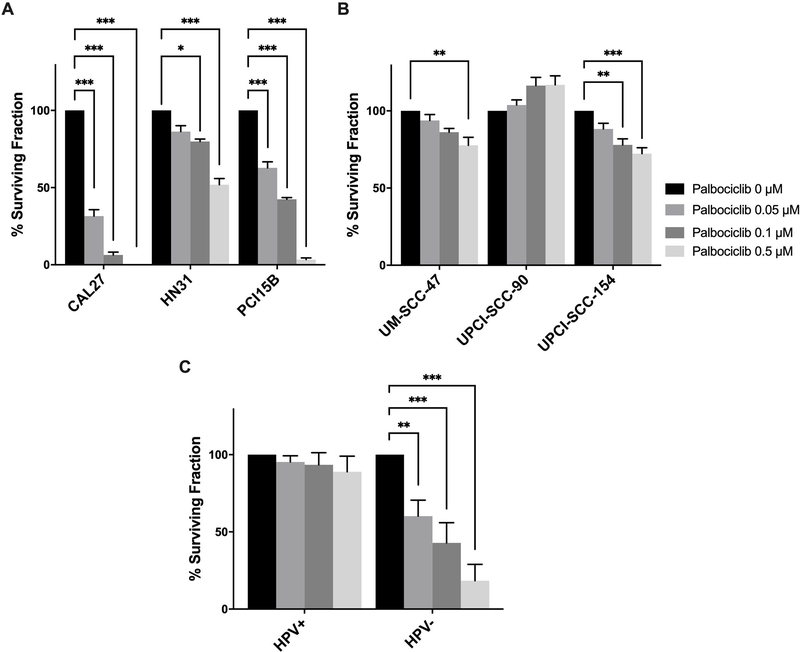
Figure 2.
Clonogenic survival of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) lines following treatment with increasing concentrations of palbociclib. Cells were incubated with 0.05, 0.1, and 0.5 μM palbociclib for 10 days (HPV- lines) or 14 days (HPV+ lines), and then assessed for colony formation. Colonies were counted and surviving fraction was standardized against the untreated control. Percent surviving fraction of each cell line is presented for each palbociclib concentration as indicated. Data presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) from three biological replicates performed on different days, with three technical replicates per biological replicate. Data are presented for HPV- (A) and HPV+ (B) HNSCC lines, as well as a pooled analysis comparing HPV+ and HPV- lines (C). Statistical significance is indicated: * if p < 0.05, ** if p < 0.01, *** if p < 0.001, comparing treatment groups with control group as determined by ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (A) and (B), and a pooled analysis comparing each treatment condition with control using a matched paired t-test (C).