Figure 7: Pre-mRNA Splicing and Partial Redundancy Within the LUC7 Family. See also Figure S7.
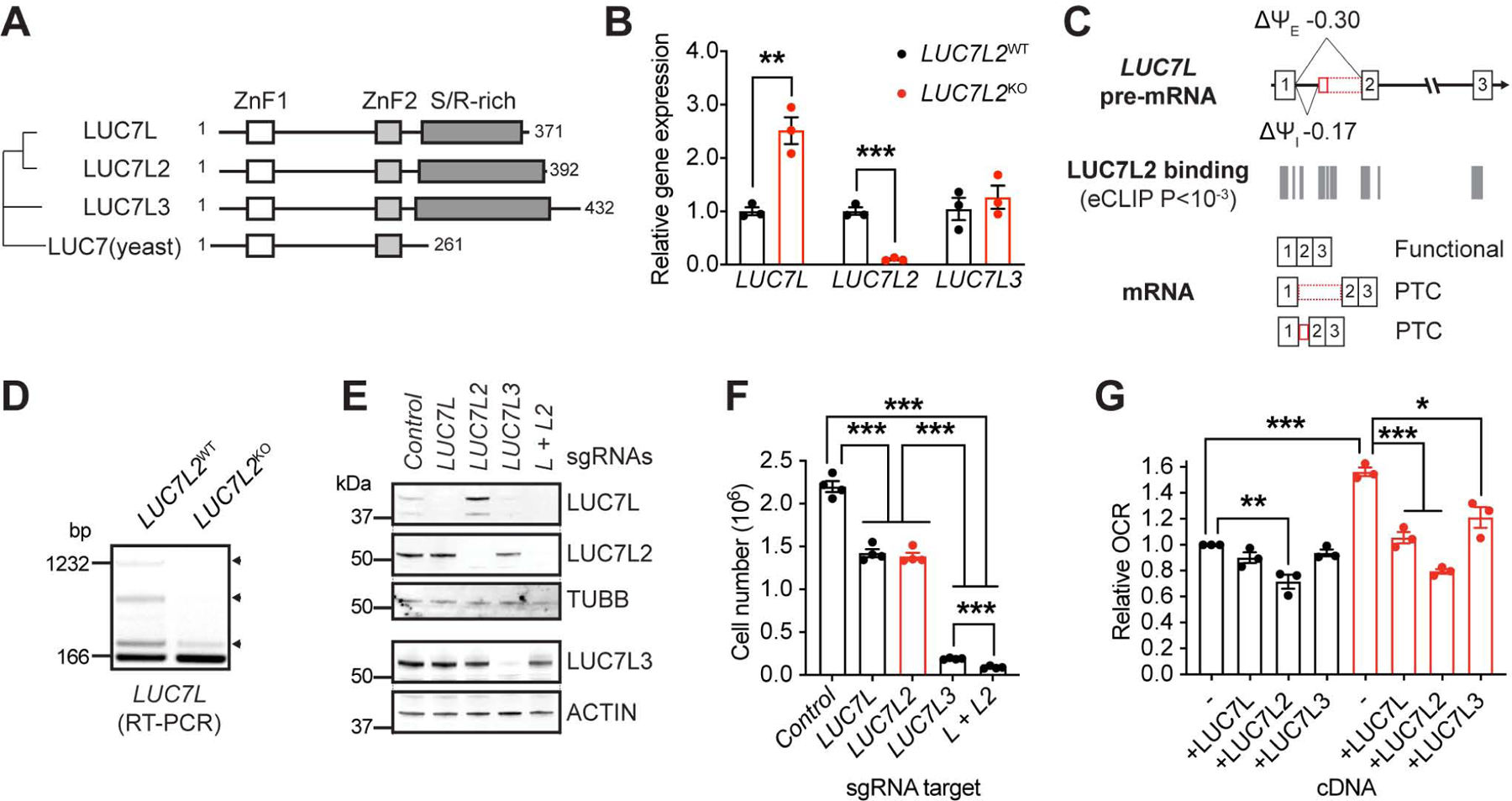
(A) Phylogenetic tree of the LUC7 protein family. LUC7 is from S. cerevisiae. ZnF: Zinc-finger domain. S/R-rich: Serine and arginine-rich domain. (B) Quantitative PCR detecting LUC7 family transcripts in LUC7L2KO K562 cells (n = 3). (C) Representation of LUC7L exons 1–3, LUC7L2 binding sites as determined by eCLIP, and the expected transcripts. Ψ: percent spliced in reported by rMATS in K562 cells. I: intron. E: exon. (D) RT-PCR amplifying LUC7L exon 1 to exon 2. Arrowheads: retained entities in LUC7L. (E) Immunoblot of LUC7 proteins in cell lines expressing Cas9 and sgRNAs targeting the indicated genes using the indicated antibodies and (F) number of cells after 4 days of growth in glucose-containing media. (G) Oxygen consumption analysis of LUC7L2KO K562 cells expressing cDNAs of LUC7 family members. All data are shown as mean ±SEM with * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, ***P<0.001, t-test relative to control.
