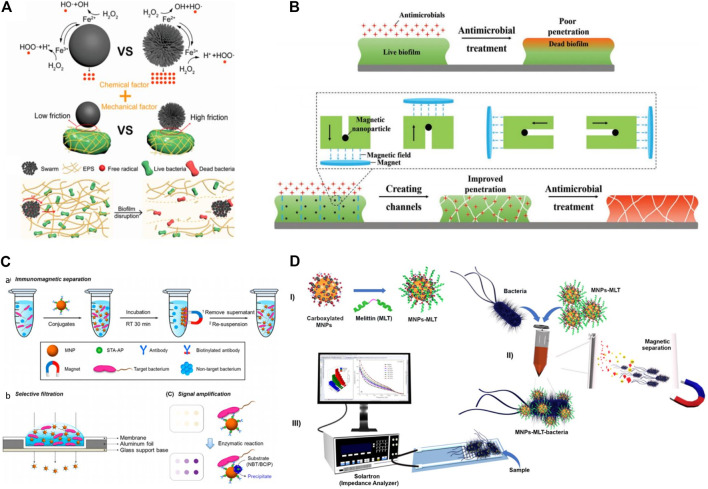
FIGURE 3.
Schematics (A) illustration of the chemical and mechanical factors of the bacteria killing of Fe3O4 and p-Fe3O4 MPs. and mechanism of biofilm disruption by a p-Fe3O4 swarm (Dong et al., 2021). Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society (B) mechanistic Representation of artificial channel created by magnetic nanoparticles in infectious biofilms to improve antimicrobial penetration and enhance bacterial killing over the depth of a biofilm (Quan et al., 2019b). Copyright 2019, John Wiley and Sons (C) Enhanced colorimetric method using enzymatic amplification with NBT/BCIP precipitation based on IMS-selective filtration for the ultrasensitive detection of E. coli O157:H7: a. IMS for target bacteria using biotinylated antibody/STA−AP/MNP conjugates, b. selective filtration of target bacteria−conjugates complexes, and c. colored spots on the filter membrane by target bacteria-bound biotinylated antibody/STA−AP/MNP conjugates (upper panel) and enhanced colorimetric spots by enzymatic amplification with NBT/BCIP precipitation on the bacteria-bound biotinylated antibody/STA−AP/MNP conjugate surfaces (lower panel) (Kim et al., 2018). Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society (D) Representation of the principle of the bioanalytical method. Functionalization of MNPs (I); capture of bacteria by MNPs-MLT and magnetic separation of the bacteria from the sample matrix (II); EIS detection (III) (Wilson et al., 2019). Copyright 2019, Elsevier publishing group.