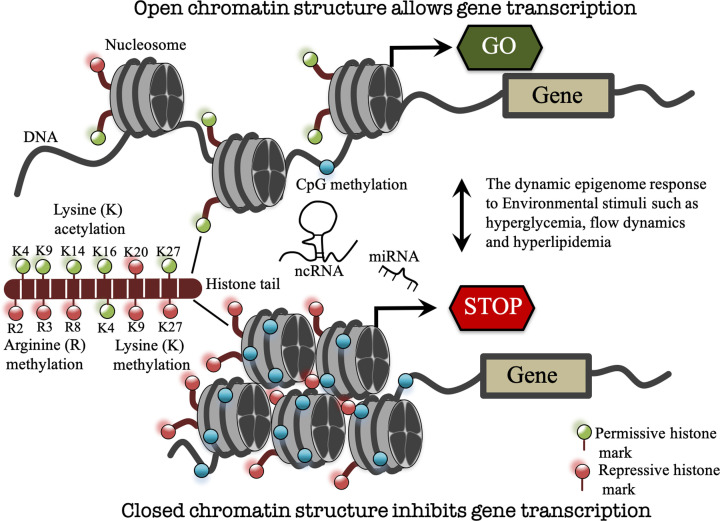
Figure 2. The dynamic epigenome.
In response to environmental cues, genes can be turned on and off by reversible epigenetic changes. Epigenetic mechanisms namely DNA methylation and histone modifications (such as arginine (R) methylation, lysine (K) acetylation/methylation (most studied and shown here) and others such as phosphorylation, ubiquitination) can alter chromatin structure from open transcription-permissive to closed transcription-repressive confirmation and vice versa. NcRNAs including lncRNAs and microRNAs (miRNAs) can also regulate gene expression at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. K, lysine followed by lysine residue position; R, arginine followed by arginine residue position.