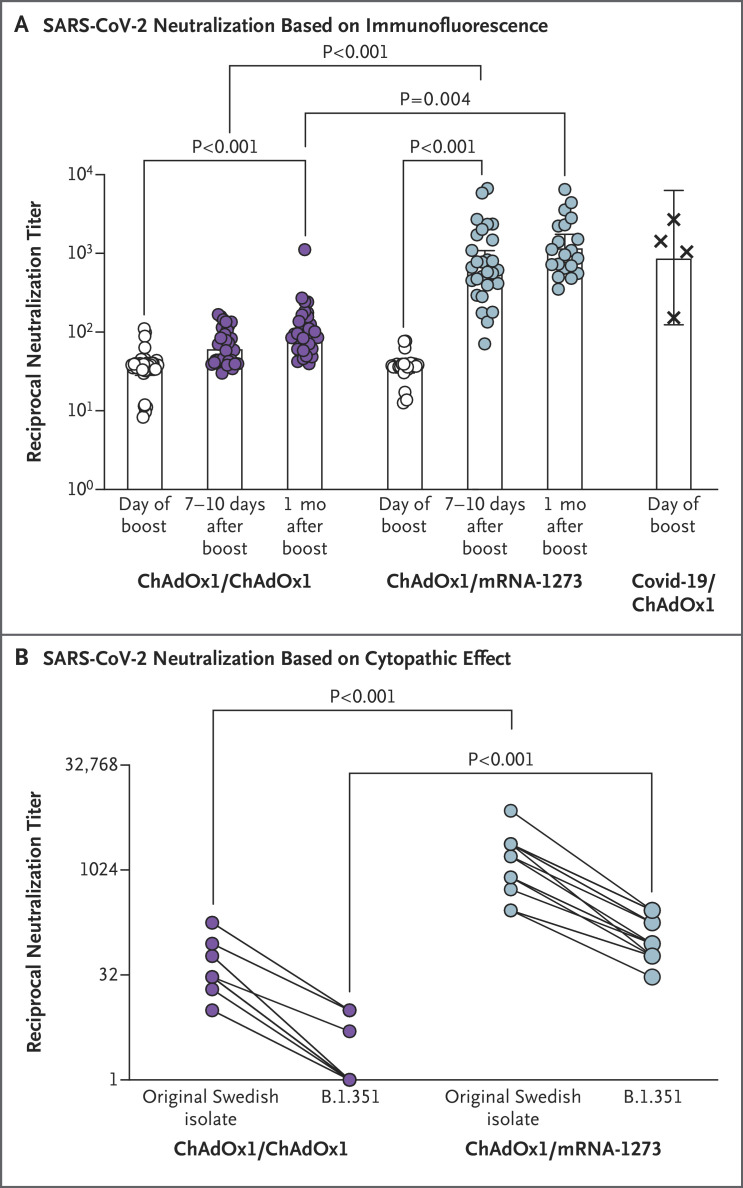
Figure 1. In Vitro Neutralization of Original SARS-CoV-2 Isolate from Sweden and the B.1.351 Variant.
Panel A shows serum neutralization of the original severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) isolate from Sweden (SARS-CoV-2/01/human/2020/SWE) on the day of the boost, 7 to 10 days later, and 1 month later. Data points are the reciprocals of the individual serum dilutions that achieved a 50% reduction in infection (reciprocal 50% inhibitory dilution) in an assay in which infection of Vero E6 cells was measured by virus-specific immunofluorescence. Bars indicate geometric means, and 𝙸 bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. In the group that received a ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 boost, the numbers of participants with specimens analyzed were 35 for the day of the boost, 34 for days 7 to 10, and 34 for 1 month; the corresponding numbers in the group that received an mRNA-1273 boost were 26, 28, and 20. As a reference, neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in 4 persons who had had coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) and had received one dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine 9 to 12 weeks before sampling were also evaluated. Panel B shows serum neutralization of the original SARS-CoV-2 isolate from Sweden and the B.1.351 variant at the 7-to-10-day time point, with neutralization evaluated as the lowest reciprocal serum dilution at which the cytopathic effect of SARS-CoV-2 on Vero E6 cells was reduced by 50% or more (50% cytopathic effect). Specimens from 18 participants in the group that received a ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 boost and from 16 participants in the group that received an mRNA-1273 boost were analyzed. All assays were performed under biosafety level 3 conditions at Umeå University (Panel A) or the Karolinska Institutet (Panel B).