Figure.
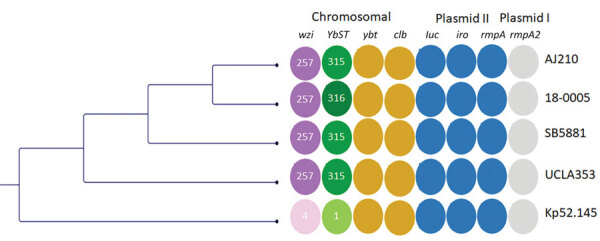
Comparative genetic analysis of sequence type 66-K2 hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate (UCLA353) from a 30-year-old man in California, USA, who had endogenous endophthalmitis and 4 other isolates: AJ210 (Australia, 2002 [6]), 18-0005 (Germany, 2017 [7]), SB5881 (France, 2018 [8]), and Kp52.145 (Indonesia, 1935 [[11]). Maximum-likelihood tree based on single-nucleotide polymorphisms and not drawn to scale. Colors indicate different loci; shades indicate different alleles. Colored columns show the capsular sequence type of the wzi gene, which codes for the outer membrane protein WZI; YbST; the chromosomal virulence loci yybt and clb; the plasmid II–associated virulence loci iuc, iro, and rmpA; and the plasmid I–associated virulence locus rmpA2. AJ210, 18-0005, SB5881 and UCLA353 share the wzi 257 allele (dark purple). AJ210, SB5881 and UCLA353 share the YbST 315 allele, whereas 18-0005 has the YbST 316 allele (dark green). The wzi and YbST alleles for strain Kp52.145 are shown in lighter colors. clb, colibactin; iro, salmochelin; iuc, aerobactin; rmpA, regulator of mucoid phenotype; YbST, yersiniabactin sequence type; ybt, yersiniabactin.
