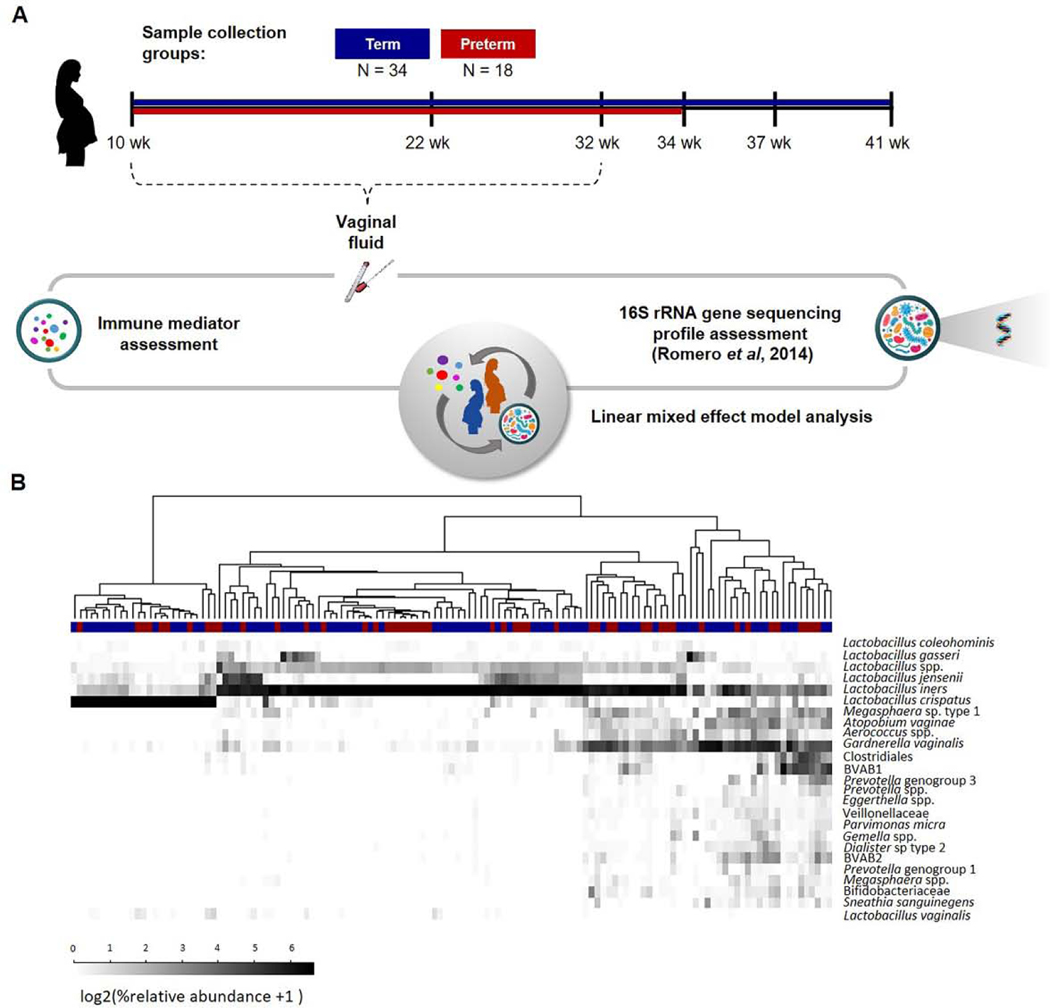
Figure 1. Study design.
(A) Samples of vaginal fluid from 52 pregnant women were collected in a case-control study: 18 delivered preterm and 34 had a term delivery. The concentrations of 33 immune mediators were determined using sensitive and specific immunoassays. For each patient, 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing data were also available. Linear mixed effect models were utilized to explore interactions between immune mediators and bacterial phylotypes in the vaginal ecosystem. (B) Relative abundances of bacterial phylotypes in the vaginal samples of women who ultimately underwent spontaneous preterm birth or delivered at term.