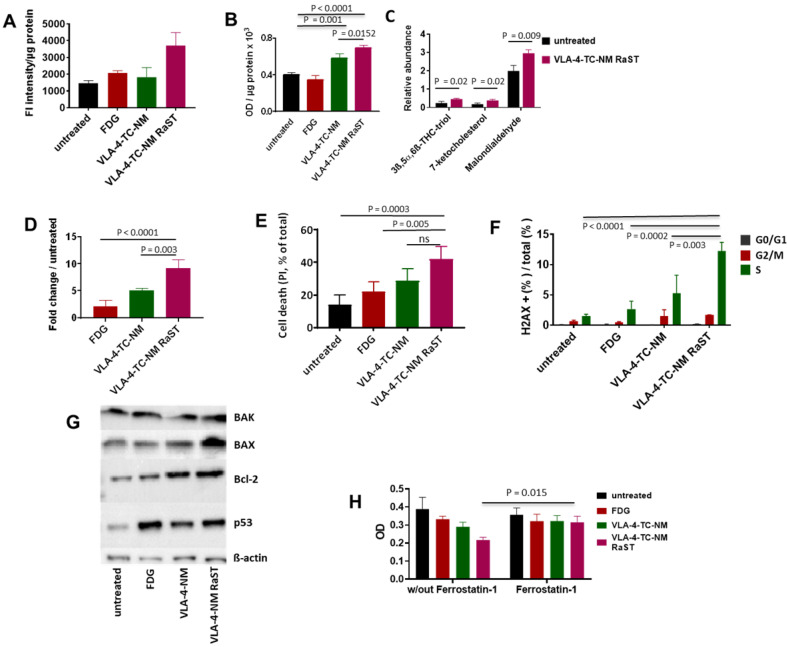
Figure 3.
Mechanism of VLA-4-TC-NM RaST. (A) VLA-4-TC-NM RaST generates significantly more ROS (P=0.0039) compared to either [18F]FDG (NS) or VLA-4-TC-NM alone (NS) when compared to no treatment; 4 x 105 MM1.S cells were treated with [18F]FDG, VLA-4-TC-NM, VLA-4-TC RaST, or left untreated. ROS measurements were performed 72 h later using H2DCFDA. (B) Hydroperoxydation of PUFA increased in cells treated with VLA-4-TC-NM RaST. MM1.S cells were plated and treated as in (A). The level of PUFA hydroperoxidation was measured with a lipid peroxidation assay 72 h later. VLA-4-TC-NM and VLA-4-TC-NM RaST produced significantly more lipid hydroperoxidation (P = 0.001 and P < 0.0001, respectively) than no treatment control. (C) VLA-4-TC-NM RaST-induced PUFA hydroperoxidation generated reactive aldehydes 72 h after administration. The cells were treated with VLA-4-TC-NM RaST or left untreated. 3ß,5α,6ß-THC-triol, 7-ketocholesterol, and malondialdehyde levels were significantly higher (P = 0.02, P = 0.02, P = 0.009, respectively) in treated cells; multiple t-tests were used for the statistical analysis. (D) Caspase-3 level was significantly higher in cells treated with VLA-4-TC-NM RaST compared to [18F]FDG and VLA-4-TC-NM (P < 0.0001 and P = 0.003, respectively) after 72 h of treatment; one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparisons tests were used for the statistical analysis. (E) Treatment of MM1.S cells with VLA-4-TC-NM RaST significantly increased the cell death (VLA-4-TC-NM RaST versus untreated: P = 0.0003; VLA-4-TC-NM RaST versus [18F]FDG: P = 0.005; VLA-4-TC-NM RaST versus VLA-4-TC-NM: NS). The cells were treated as in (A). After 72 h, the cells were treated with 0.1 µg PI, and the amount of cell-associated PI was determined with Flow Cytometry; one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparisons tests were used for the statistical analysis. (F) dsDNA breaks were significantly more abundant 72 h after VLA-4-TC-NM RaST. The cells were treated as in (A). After 72 h, the cells were stained with anti-γH2AX and DAPI. Flow Cytometry analysis showed an overall increase in dsDNA breaks during the S-phase. Specifically, dsDNA breaks were significantly more frequent during VLA-4-TC-NM RaST treatment compared to VLA-4-TC-NM (P = 0.003), [18F]FDG (P = 0.0002), and the untreated cells (P < 0.0001); 2way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparisons tests were used for the statistical analysis. (G) Western blotting showed increased levels of apoptosis-related proteins 72 h after VLA-4-TC-NM RaST. The cells were treated as in (A). (H) Ferroptosis inhibitor Ferrostatin-1 significantly inhibited VLA-4-TC RaST mediated cell death (P = 0.015). MM1.S cells were plated as in (C). Ferrostatin-1 was administered concomitantly with VLA-4-TC RaST and VLA-4 control at the final concentration of 10 µM. Three-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparisons tests were used for statistical analyses.