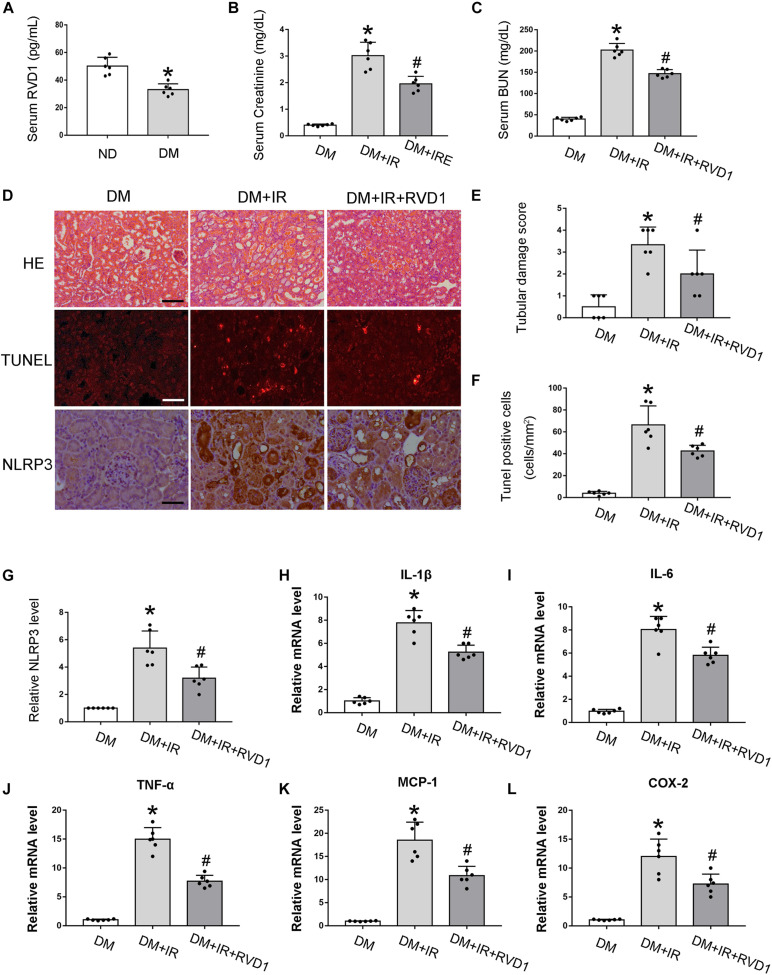
FIGURE 3.
Resolvin D1 (RvD1) attenuated susceptibility to ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI) in diabetes. Male C57BL/6J mice were injected with streptozotocin (STZ) or vehicle solution to induce diabetic mice (DM) or non-diabetic mice (ND). The mice were then subjected to sham operation or 30 min of bilateral renal ischemia followed by 48 h of reperfusion (I/R48). (A) Serum RvD1 levels detected by ELISA. All the data are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 6). *p < 0.05 vs. the relevant ND group. (B,C) Serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN). (D) Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining for renal tissues. Scale bar, 100 μm. TUNEL assay to reveal apoptosis of renal tissues: scale bar, 50 μm. Immunohistochemistry of NLRP3: scale bar, 50 μm. (E) Semi-quantification for renal tissue damage. (F) Statistical analysis for TUNEL-positive cells. (G) Semi-quantification for NLPR3 expression. (H–L) Real-time PCR for IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, and COX-2. All the data in (B,C,E–L) are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 6). *p < 0.05 vs. the relevant DM group; #p < 0.05 vs. the relevant DM + I/R group.