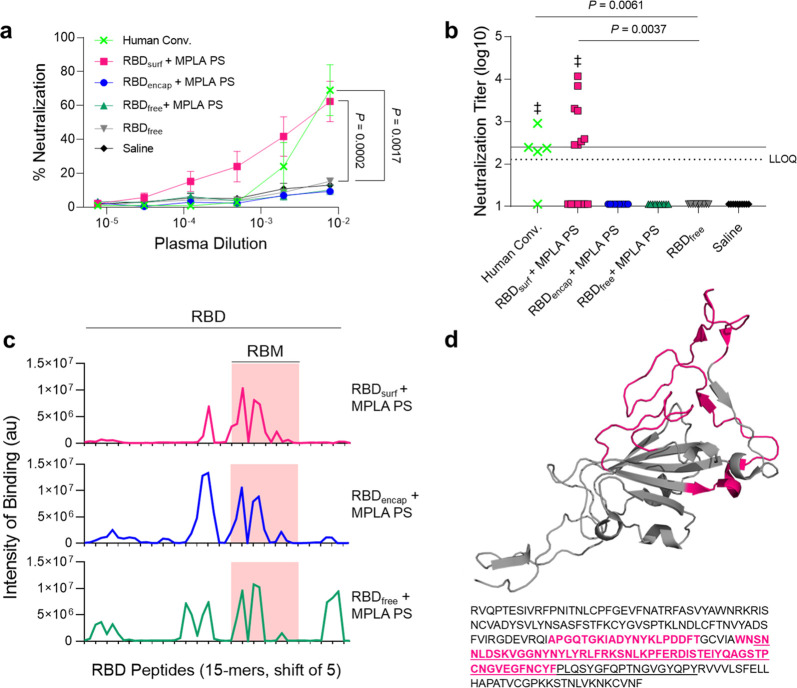
Figure 3.
Antibodies induced by vaccination with RBDsurf + MPLA PS are neutralizing and localized to the receptor-binding motif. (a) Plasma from mice 1 week postboost was tested for its ability to neutralize SARS-CoV-2 infection of Vero E6 cells in vitro. Percent neutralization for multiple plasma dilutions normalized to cells without virus (100%) or without plasma (0%). Data plotted as mean ± SEM for n = 5 human convalescent samples (human conv.) or 10–15 mice. Comparisons to unadjuvanted RBDfree were made for lowest dilution (10–2.11) using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test. (b) Virus neutralization titers, representing the plasma dilution at which 50% of SARS-CoV-2-mediated cell death is neutralized. Dashed line: lower limit of quantification (LLOQ = 2.11). For values below the LLOQ, LLOQ/2 values were plotted. Solid line: FDA recommendation for “high titer” classification (=2.40). Comparisons were made using a Kruskal–Wallis nonparametric test with Dunn’s post-test or a Wilcoxon signed rank test (‡ ns, P > 0.05 compared to hypothetical value of 2.40). Symbols represent individual mice. (c) Pooled plasma was then tested for antibody binding to linear epitopes using overlapping 15-amino-acid peptides with 5-amino-acid offsets, spanning the entire RBD sequence. The x-axis represents sequential peptide number within the RBD amino acid sequence showing the position of the receptor-binding motif (RBM), and the y-axis represents average luminescence for each peptide epitope. (d) 3D structure and amino acid sequence of RBD with the RBM underlined and main peptide sequences recognized by mouse plasma highlighted in pink (Protein Data Bank Entry 7DDD).