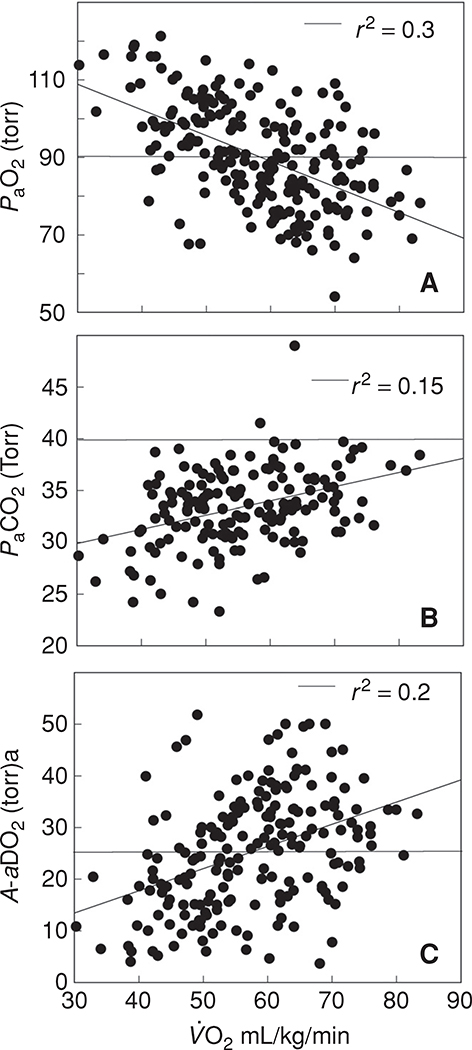
Figure 6.
Temperature corrected arterial blood gases obtained at near maximal and maximal exercise (cycle ergometer or treadmill running) in normal subjects [(A) n = 198; (B) and (C) n = 175)]. Data are, with permission, from references (15, 45, 76, 93, 94, 118, 121, 124, 219, 231, 251, 328, 357). The horizontal line in A and B defines the normal value and in C the limits of the expected increase in A-aDO2 with exercise as defined by Dempsey and Wagner (47). The arterial PO2 is lower and the PaCO2 and A-aDO2 higher with increasing aerobic capacity. Above a of 65 to 70 mL/kg/min the majority of individuals have significant gas exchange impairment although it is uncommon in individuals with a .