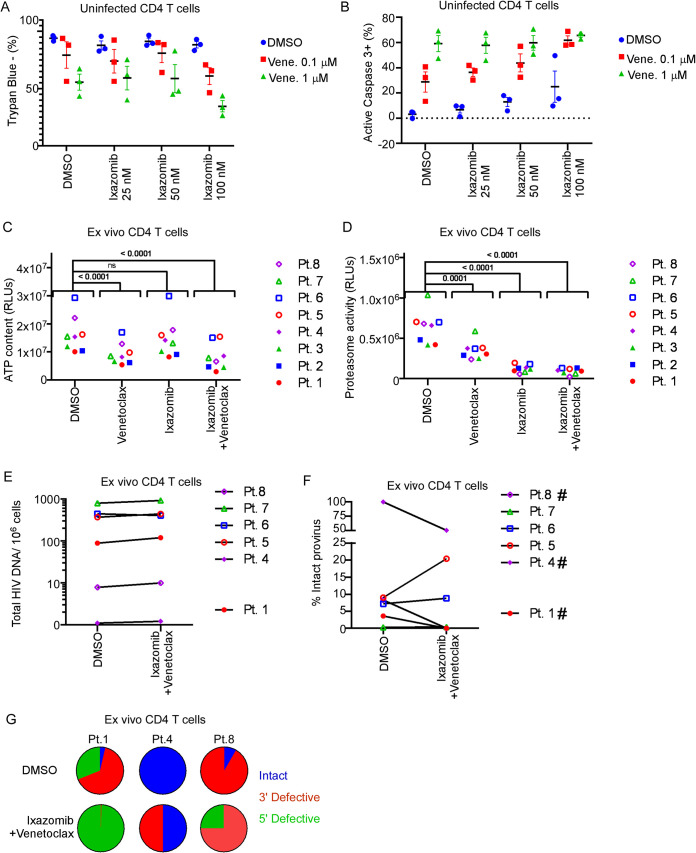
FIG 4.
Ixazomib plus venetoclax reduces intact HIV provirus in ex vivo CD4 T cells in a subset of participants. (A and B) CD4 T cells from 3 uninfected donors were treated with increasing concentrations of venetoclax (venet.) and/or ixazomib and assessed for viability by trypan blue exclusion (A) or apoptosis by active caspase 3 expression (B). CD4 T cells from 8 ART-suppressed, HIV-positive participants were treated ex vivo with venetoclax (100 nM), ixazomib (25 nM), or the combination for 72 h in the presence of ART to prevent spreading infection. (C) Treated CD4 T cells were assessed for viability by ATP content at 72 h. (D) Treated CD4 T cells were assessed for proteasome activity at 72 h. (E and F) Total and intact cell associated HIV provirus was measured at 72 h by IPDA. (F) The percentage of the total HIV provirus that was intact provirus is depicted for 6 of 8 participants. Two samples were excluded due to technical failure. (G) Proportions of intact (blue), 3′ defective (red), and 5′ defective (green) provirus from participants 1, 4, and 8.