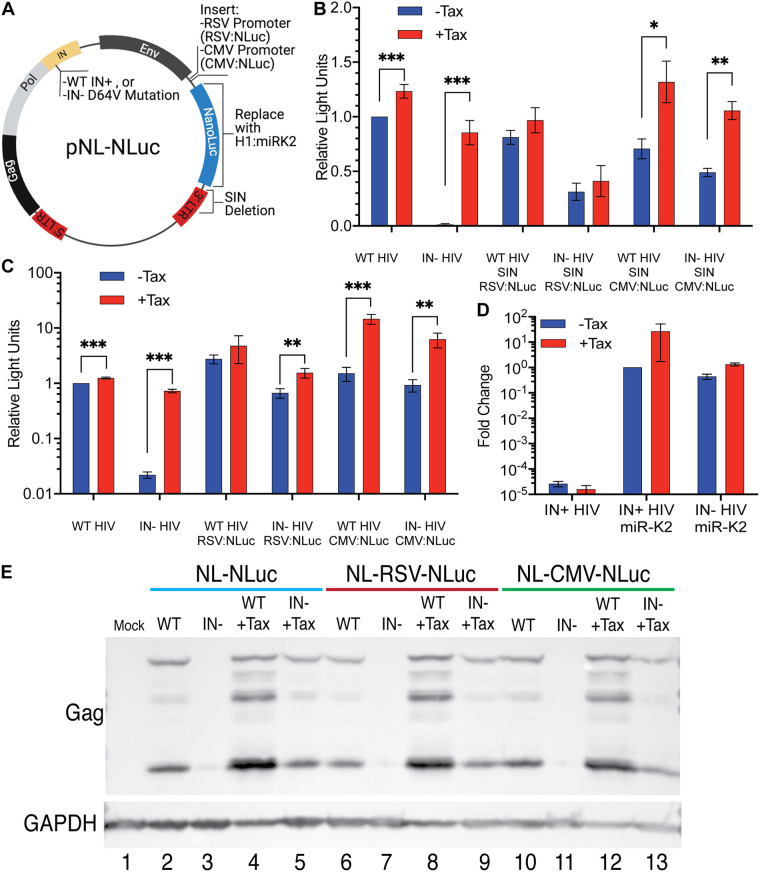
FIG 4.
Unlike the HIV-1 LTR, heterologous internal Pol II and Pol III promoters are not silenced on unintegrated HIV-1 proviruses. (A) Schematic of pNL-NLuc and its derivatives. (B) CEM-SS cells with and without Tax were infected with IN+ or IN− HIV-1 variants expressing NLuc from the viral LTR or with self-inactivating (SIN) derivatives lacking the LTR U3 region from −18 to −418, including the HIV-1 promoter and enhancer. Instead, these viruses express NLuc from an internal RSV LTR promoter (that has no NF-κB binding sites) or an internal CMV promoter (that has NF-κB binding sites). Nevirapine was added at 16 hpi to prevent virus spread, and cells were harvested for NLuc assays at 48 hpi. NLuc activity was normalized to WT NL-NLuc activity in the absence of Tax, which was set to 1. (C) Similar to panel B but using a non-SIN vector design. (D) CEM-SS cells with and without Tax were infected with WT or IN− virus expressing KSHV miR-K2 from the Pol III-dependent H1 promoter. Nevirapine was added to the cells at 16 hpi, and the cells were harvested for quantification of miR-K2 by qRT-PCR at 48 hpi. Endogenous U6 RNA served as an internal control, and data were normalized to WT minus Tax, which was set to 1. n = 3 biological replicates. Error bars show SD. (E) HIV-1 Gag expression levels in CEM-SS cells with and without Tax infected with the indicated WT or IN− viruses. Endogenous GAPDH was used as a loading control. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01, and ***, P < 0.001, calculated using an unpaired Holm-Šidák multiple-comparison t test.