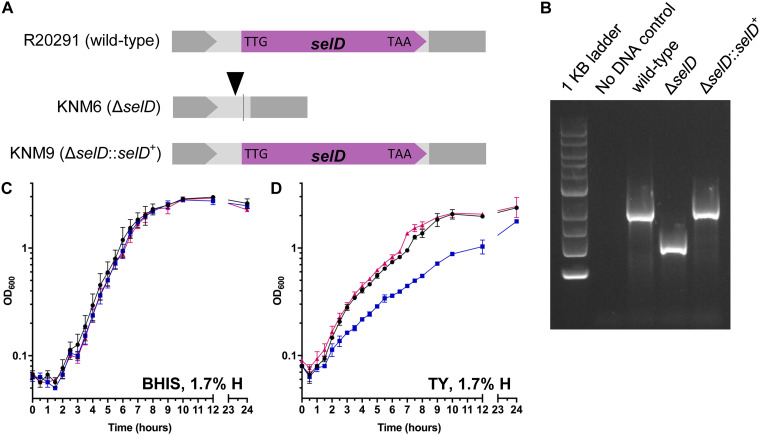
FIG 2.
Insertion by C. difficile CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing tool and the slight growth defect of a C. difficile ΔselD strain. (A) Graphical representations of the three strains used in this study. Shown as a triangle is the target site of the gRNA, and the line indicates the site of the deletion. (B) DNA was isolated from C. difficile R20291 (wild type), KNM6 (ΔselD), and KNM9 (ΔselD::selD+). The region surrounding the selD gene was amplified from the chromosome, and the resulting DNA was separated on an agarose gel. A clean deletion of selD is indicated by a faster-migrating DNA band while wild type and the insertion mutation (restoration) are indicated by a slower-migrating DNA band. (C and D) C. difficile R20291 (wild type) (●), C. difficile KNM6 (ΔselD) (■), and C. difficile KNM9 (ΔselD::selD+) (▲) were grown in (■) BHIS medium (C) and TY medium (D) at 1.7% hydrogen, and growth was monitored over a 24-h period. Data points represent the average from three independent experiments and error bars represent the standard deviation from the mean.