FIG 1.
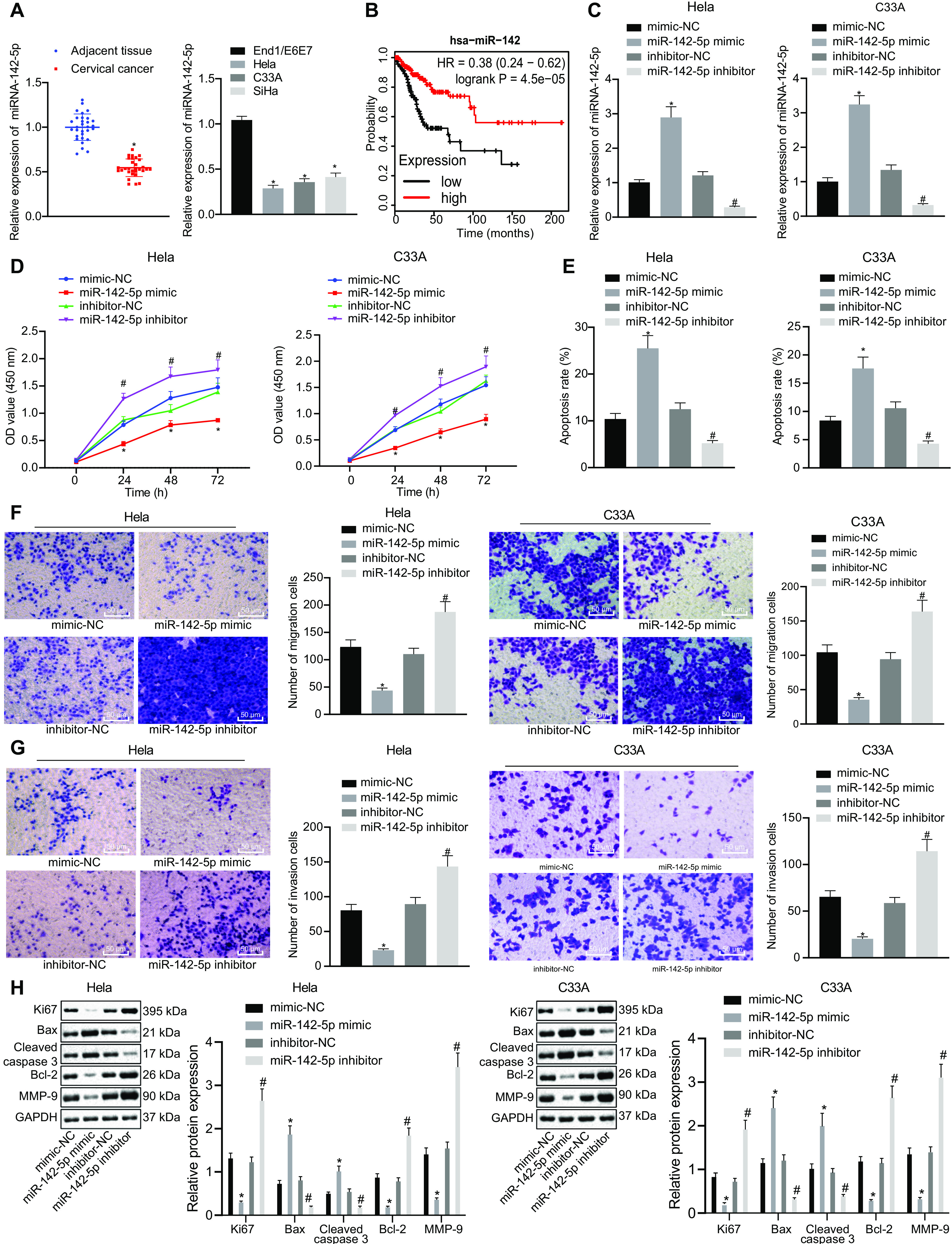
miR-142-5p is poorly expressed in cervical cancer tissues and cells, and overexpression of miR-142-5p inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of cancer cells and promotes apoptosis. HeLa and C33A were transfected with miR-142-5p mimic or miR-142-5p inhibitor. (A) The expression of miR-142-5p in the clinical tissues and cells of cervical cancer was detected by RT-qPCR (n = 30). (B) Survival analysis of miR-142 in the clinical treatment of TCGA cervical cancer. The x axis represents the survival time, and the y axis represents the survival rate, with red indicating the survival status of patients with high expression and black indicating the survival status of patients with low expression. (C) miR-142-5p expression in the transfected HeLa and C33A cells was measured using RT-qPCR. (D) Proliferation was detected using CCK-8. (E) Apoptosis was examined by flow cytometry. (F and G) Migration and invasion were tested using the Transwell assay (×200). (H) The expression of related genes was monitored by Western blot analysis. The measurement data are expressed as means ± standard deviations. The paired t test was used to compare the carcinoma and adjacent tissues. The data comparison between multiple groups was performed using ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. For data comparison between groups at different time points, repeated-measurement ANOVA was used, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. *, P < 0.05 versus adjacent tissues or mimic-NC-transfected HeLa and C33A cells; #, P < 0.05 versus inhibitor-NC-transfected HeLa and C33A cells.
