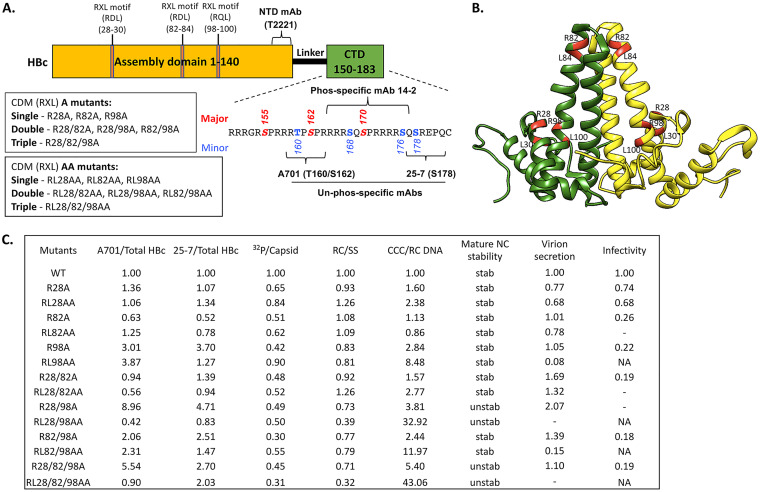
FIG 1.
Summary of the HBc CDM mutants and their phenotypes. (A) Schematic of HBc protein structure highlighting key domains, residues, and MAb epitopes. The NTD, linker, and CTD are indicated. The multiple RXL motifs in the assembly domain (NTD) of HBc at positions 28 to 30, 82 to 84, and 98 to 100 are indicated. The CDM A and CDM AA mutants are described, as is the CTD sequence (positions 150 to 183), with the three major S/T-P phosphorylation motifs (S155, S162, S170) and four minor sites of CTD phosphorylation highlighted. The epitopes/regions recognized by the indicated MAbs are also shown. (B) Localization of the three CDM sites (with the conserved R and L residues in each motif) highlighted in red on the HBc dimer structure (NCBI Protein ID 6HTX) (71). (C) Summary of the effects of the HBc CDM (RXL) mutations on HBc CTD phosphorylation, endogenous kinase activity, and HBV replication in HepG2 cells. The levels of HBc protein that were nonphosphorylated at T160/S162 (within the A701 epitope) or S178 (within the 25-7 epitope) were normalized to total HBc detected by the NTD MAb T2221. The endogenous kinase activity detected by 32P labeling was normalized to the total capsid amount detected by the NTD MAb T2221. RC DNA was normalized to SS DNA as a measure for RC DNA synthesis/stability. The CCC DNA amount normalized to RC DNA represents CCC DNA synthesis efficiency. Mature NC stability was tested by DNase digestion of RC DNA. The DNA virion level was normalized to the intracellular RC DNA amount as a measure of virion secretion efficiency. Viral infectivity was defined by the CCC DNA amount produced during infection by using the same MOI. The normalized level for each parameter from the WT HBc is set at 1.00. unstab, unstable NC; stab, stable NC (similar to WT); NA, not applicable (not enough virion available to assess infectivity); −, undetectable.