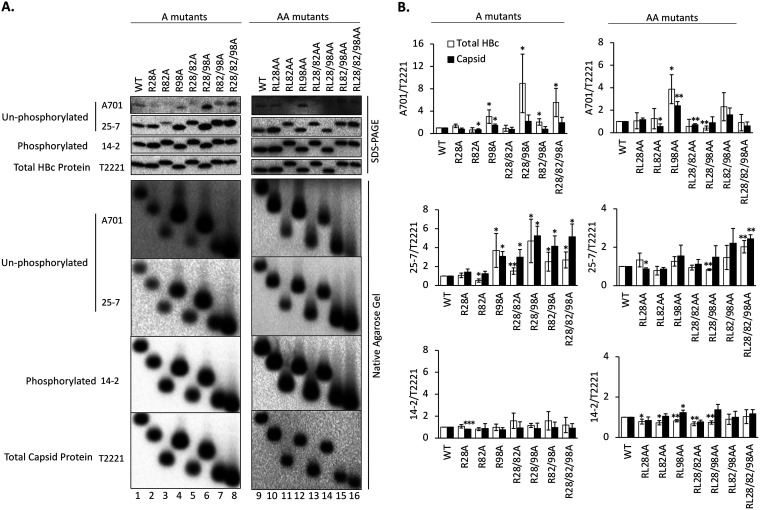
FIG 2.
Effects of the HBc CDM mutations on HBc CTD phosphorylation state. HepG2 cells were transfected with the indicated HBc expression constructs. Five days later, the cytoplasmic lysates were collected. (A) Levels of HBc (top) or assembled capsid (bottom) were measured following SDS-PAGE and transfer to a PVDF membrane or agarose gel electrophoresis and transfer to a nitrocellulose membrane, respectively, using the indicated MAbs. MAb A701 or 25-7 specifically recognizes HBc CTD unphosphorylated at T160 (possibly also S162) or S178, respectively. MAb 14-2 recognizes CTD phosphorylated at S170. Total HBc or capsid levels were determined by the NTD-specific MAb T2221. (B) The A701, 25-7, or 14-2 signals were normalized to the T2221 signals for each CDM mutant or WT HBc, and the normalized values are expressed relative to that of the WT, which was set at 1.00. Total HBc levels (i.e., assembled and nonassembled), either phosphorylated as detected by MAb 14-2 or dephosphorylated as detected by MAb A701 or 25-7, after normalization to all HBc as detected by MAb T2221 were derived from SDS-PAGE Western blots. Similarly, capsid levels (assembled capsids) were derived from native agarose gel electrophoresis/Western blots. Data are presented as the mean and SD of results from at least three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant differences in comparison with the WT (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).