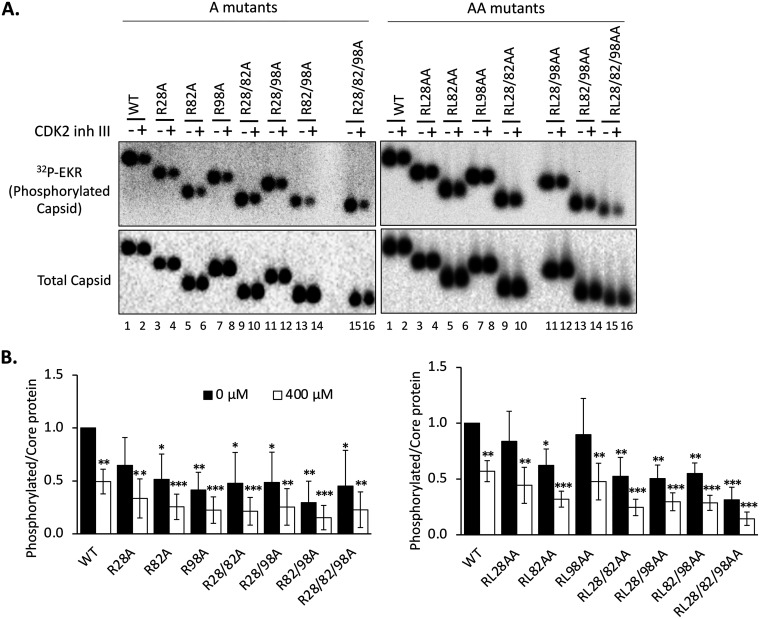
FIG 4.
Effect of the HBc CDM mutations on the endogenous kinase activity in capsids. (A) HepG2 cells were transfected and harvested as described in the legend to Fig. 2. An in vitro endogenous kinase reaction (EKR) assay was conducted with the indicated HBV capsids without or with 400 μM CDK2 inhibitor III (inh III). The reaction products were resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis, phosphorylated capsids labeled by the endogenous kinase were detected by autoradiography (top panel), and total capsid levels were measured by Western blot analysis by using the HBc MAb T2221 (bottom). (B) The effects of the CDM mutations on the EKR efficiency were calculated by normalizing the phosphorylation (32P) signal of the WT HBc or CDM mutants, with or without the inhibitor, to the respective capsid level and are expressed relative to the normalized signal of the WT capsid in the absence of the inhibitor, which was set at 1.0. Data are presented as the mean and SD of results from three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant differences in comparison with the WT (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).