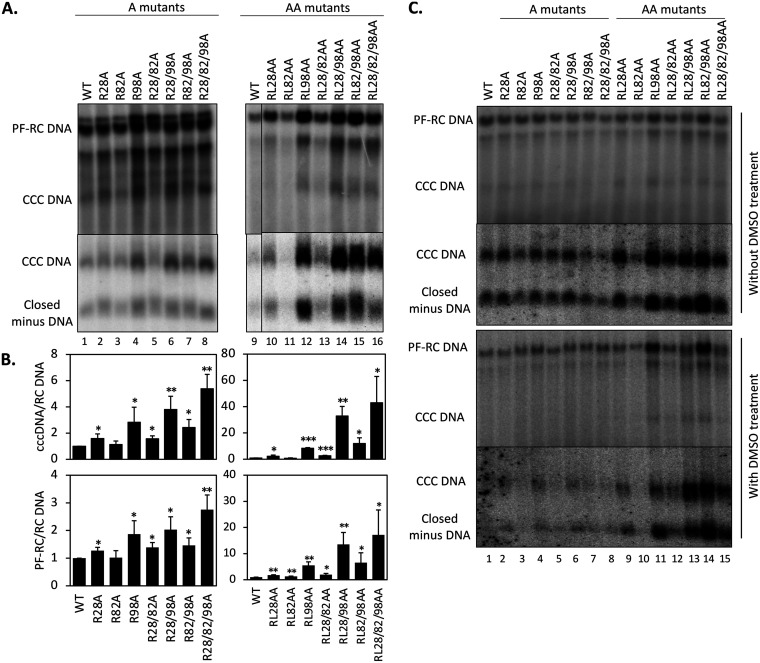
FIG 7.
Effects of the HBc CDM mutations on CCC DNA formation. HepG2 cells were transfected and harvested as described in the legend to Fig. 5. (A) PF DNA, including PF-RC and CCC DNA, was purified and digested by DpnI as described in Materials and Methods to remove plasmid DNA copurifying with the HBV PF DNA (top panel). HBV PF DNA was further treated with Exo I and III to remove noncovalently closed DNA for specific detection of CCC DNA (bottom panel). (B) CCC DNA levels (top panel) and PF-RC DNA levels (bottom panel) from the WT and mutants were normalized to those of core RC DNA. Normalized CCC DNA or PF-RC DNA level from the mutants was compared to that of the WT, which was set at 1.0. Data are presented as the mean and SD of results from three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate significant differences in comparison with the WT (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (C) HepG2-NTCP cells were transfected and harvested as described in the legend to Fig. 5. PF DNA was extracted from transfected HepG2-NTCP cells cultured without (top two panels) or with (bottom two panels) supplementation with 2% DMSO after transfection. DNA was analyzed by Southern blot analysis. Closed minus-strand DNA was derived from PF-RC DNA in which the minus strand is covalently closed but the plus strand remains open (60).