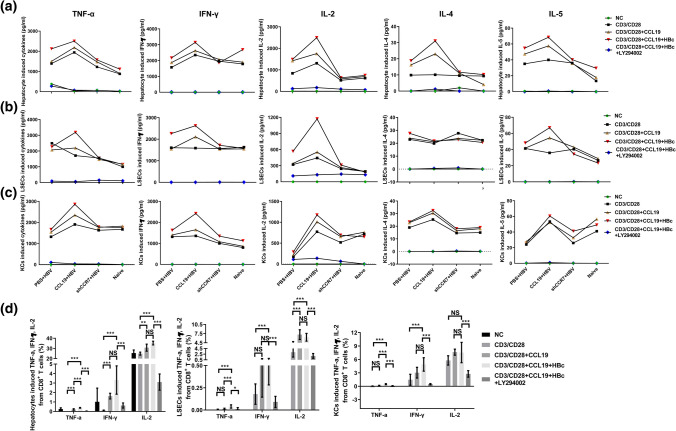
Fig. 4.
CCL19 mediates reversing the suppressive properties of hepatocytes and NPCs to induce T-cell immunity and secretive cytokines. C57BL/6 mice were injected with PBS, CCL19 and shCCR7 plus pAAV-HBV1.2, separately. After 60 dpi, hepatic APCs (hepatocytes, CD146+ LSECs and F4/80+ KCs) were separated by centrifugation and MACS sorting and then treated with or without 100 ng/ml murine CCL19 protein stimulated hepatocytes, LSECs or KCs were incubated 24 h. Then, after discarding the supernatants and washing the cells, fresh splenocytes from experimental gourps stimulated with anti-CD3 (1 μg/ml) and anti-CD28 (1 μg/ml) were added (2 × 106/well), and the cells were co-cultured at a ratio of 1:2 (APCs: splenocytes). The supernatants from co-cultivation for 48 h with hepatocytes (a), LSECs (b) and KCs (c) were analyzed by flow cytometry for the Ag-responsive TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4 and IL-5. d Intracellular cytokines of CD8+ T cells involved in TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-2 production were assessed by flow cytometry in CCL19 + HBV group. The data are shown as superimposed symbols at the mean with connecting lines of one out of two representative experiments, which were performed in triplicate wells. Five mice were analyzed per group, and at least two independent experiments were performed. The data are presented as the means ± SEMs in panels. Significant differences between the groups are indicated: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; NS not significant