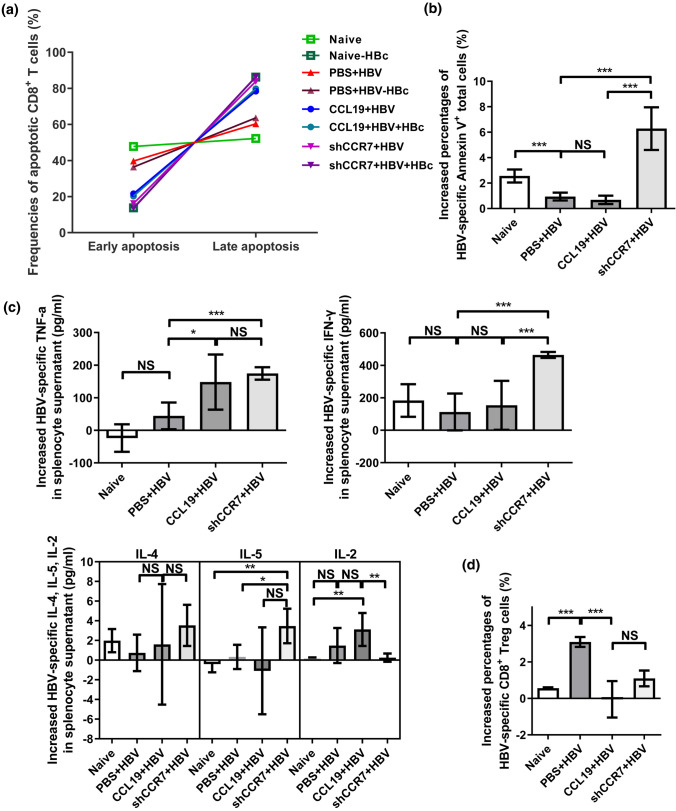
Fig. 5.
CCL19 mediates Ag-responsive CD8+ T cells apoptosis, Treg cells and secretive cytokines. Freshly isolated splenocytes of the three CHB mouse models were collected at 60 dpi, stimulated with anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28 and HBc peptide in vitro, and then cultured for 48 h at 37 °C in an incubator under an atmosphere with 5% CO2. Annexin V+/PI+ CD8+ T cells were detected by flow cytometry. Early apoptosis: FITC-Annexin V (+) and BV510-PI (−); late apoptosis: FITC-Annexin V (+) and BV510-PI (+). a Detection of the apoptotic lymphocytes (CD8+ T cells) after HBc peptide stimulation in vitro. b Increased percentages of HBV-induced late apoptotic (Annexin V+) total cells (CD4+ plus CD8+ T cells). c Increased levels of cytokines in the supernatants of splenocytes were assessed by flow cytometry after with and without HBc peptide stimulation in vitro. d Increased CD8+ Treg cells were detected by flow cytometry after with and without HBc peptide stimulation. The data are presented as the means ± SEMs of one out of two representative experiments, which were performed in triplicate wells. Increased percentage of apoptotic cells or Treg cells (%) = (frequencies(murine splenocytes + HBc)—frequencies(murine splenocytes))/frequencies(murine splenocytes) × 100 (%); Increased cytokines = doses (murine splenocytes + HBc)—doses(murine splenocytes). Five mice were analyzed per group, and at least two independent experiments were performed. Significant differences between the groups are indicated: *p < 0.05; **p< 0.01; ***p < 0.001; NS not significant