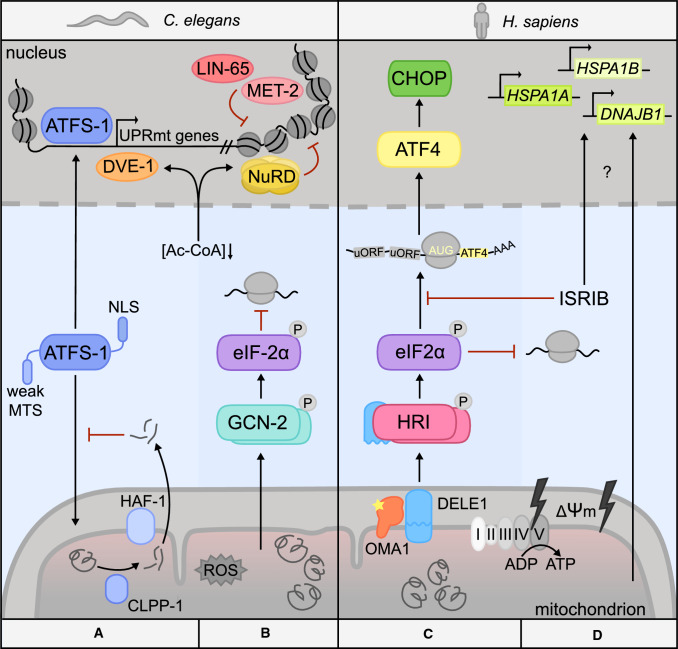
Fig. 2.
Principal response modules against stress originating from the mitochondrial interior in worms and humans. Differences and similarities in the response to mitochondrial dysfunction in C. elegans and H. sapiens. A UPRmt gene expression in worms is dependent on two stress signals: mitochondrial import efficiency and metabolic cues such as decreased acetyl coenzyme A (Ac-CoA) levels due to reduced mitochondrial TCA cycle activity. ATFS-1 acts as a sensor of mitochondrial import efficiency due to its weak MTS. Under conditions of perturbed import, ATFS-1 is imported into the nucleus via its NLS and activates transcription of UPRmt genes with the help of DVE-1 and its cofactor UBL-5. While histone demethylases JMJD-1.2/3.1 increase accessibility of UPRmt genes, LIN-65, MET-2 and NuRD complex members promote a global chromatin compaction through histone methylation and deacetylation and thus reduce the expression of other genes. Reduced TCA cycle activity during mitochondrial stress lowers cellular levels of Ac-CoA, which facilitates chromatin reorganization through nuclear recruitment of NuRD and DVE-1. B A cytoprotective translation attenuation is induced through GCN-2 activation and eIF2α phosphorylation. C In human cells, a diverse array of mitochondrial insults activates the mitoprotease OMA1, which in turn cleaves the mitochondria-resident factor DELE1. The C-terminal cleavage product (S-DELE1) subsequently accumulates in the cytosol, where it binds and activates the eIF2α kinase HRI. The resulting ISR signaling leads to a global attenuation of translation, while favoring expression of uORF-containing ISR master regulators like ATF4 and CHOP. D Unproductive ISR signaling in the context of mitochondrial stress because of genetic deficiencies in DELE1, HRI or pharmacological manipulation of eIF2B (ISRIB) results in the activation of a program dominated by heat shock protein expression