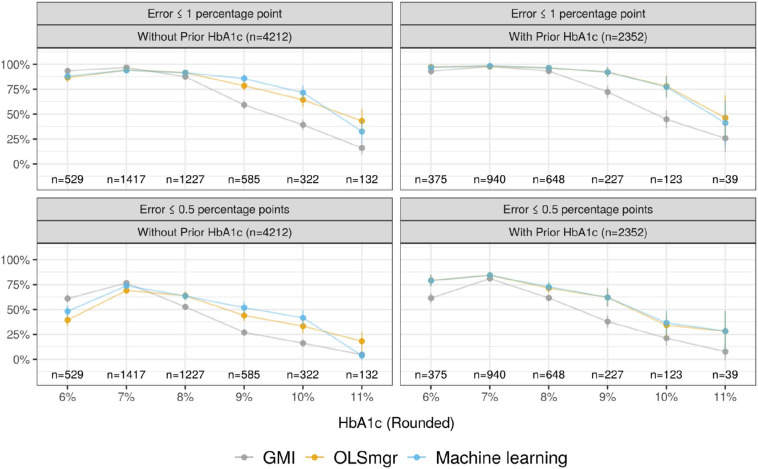
Fig. 1.
For each HbA1c value rounded to the nearest whole number, the plots show the proportion of model estimates that were within 1 percentage point (top) and 0.5 percentage points (bottom) of true HbA1c, with 95% confidence intervals for each proportion. Non-overlapping confidence intervals indicate statistical significance at the 0.05 level. The left plots compare GMI to an OLS model accounting for race and mean glucose (OLSmgr) and a random forest (RF) model accounting for many CGM metrics and demographics (Machine learning). The right plots compare GMI to OLSmgr fit with prior HbA1c and a LASSO model accounting for prior HbA1c along with the same covariates as the RF model (Machine learning). The sample sizes indicate the number of HbA1c values that fall in each rounded HbA1c bucket.