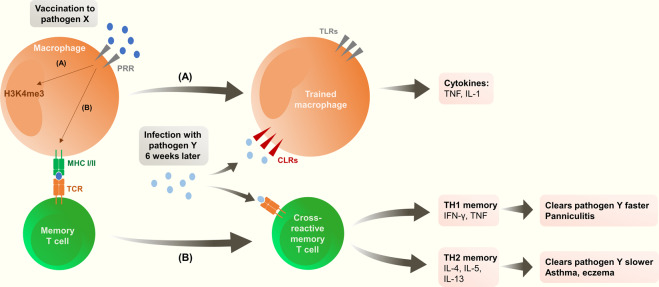
Fig. 3. Possible immunological mechanisms explaining downstream effects of vaccination (adapted from Benn 2013).
After vaccination for pathogen X two possible pathways may explain downstream effects: A Epigenetic re-programming of monocytes/macrophages leading to a more rapid activation after exposure to pathogen Y, to ensure rapid clearance of this pathogen. B T cell-mediated cross-reactivity: memory CD4 and CD8 T cells are generated that are cross-reactive with pathogen Y. PRR pattern recognition receptors, MHC major histocompatibility complex, TLR Toll-like receptors, CLR C-type lectin receptors, TCR T cell receptor.