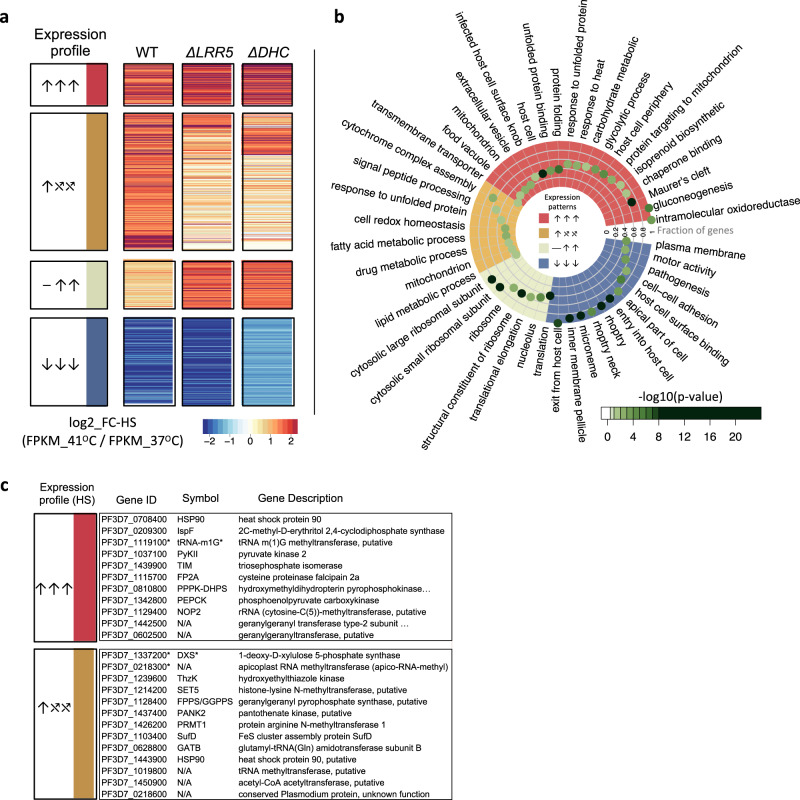
Fig. 3. Unfolded-protein response, apicoplast-targeted, and mitochondria-targeted stress-response pathways are critically dysregulated in functionally unrelated HS-Sensitive mutant clones.
a Genes were classified into three different categories based on NF54-expression with and without HS-exposure across all three parasite lines (Supplementary Data File 3, “Methods” section): upregulated in HS (↑, n = 415), downregulated in HS (↓, n = 611), or not regulated by HS (⎯, n = 1541). Genes expressed above threshold in NF54 and both HS-Sensitive mutants (n = 1298) were then assigned into six HS expression categories based on phenotype in NF54 vs. mutants ΔLRR5 and ΔDHC. HS-regulated genes shared between NF54 and both mutants are indicated in red (↑↑↑, n = 94) or blue (↓↓↓, n = 205) for upregulated and downregulated genes, respectively. Genes dysregulated in one or both HS-Sensitive mutants fell into two main expression-profile categories: those upregulated in NF54 that failed to be regulated in the mutants (↑⤯⤯, n = 83), and genes not regulated in response to HS in NF54 that were inappropriately upregulated in the mutants (⎯ ↑↑, n = 74). Most remaining genes were not regulated in response to HS in any parasite line (n = 615). b Functional enrichment analyses between wild-type/mutant HS-expression profiles. Red: Shared upregulated HS-responsive GO-terms between NF54 and the two HS-Sensitive pB-mutants (↑↑↑). Blue: Shared downregulated GO-terms (↓↓↓). Ocher: GO-terms upregulated in NF54 but dysregulated in both mutants (↑⤯⤯). Tan: GO-terms enriched in genes not regulated in the wild-type HS-response but upregulated in the mutants (⎯ ↑↑). Only enriched GO-terms are shown (two-tailed Fisher/elim-hybrid test p-value ≤ 0.05), with the highest significance indicated in dark green. Fraction of significant genes mapping to a GO-term in an HS expression-profile category vs. genes mapping to that GO-term in the entire analysis is indicated by distance to the center of the circle. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. c Several apicoplasts and isoprenoid biosynthesis-related genes were upregulated in the wild-type response to HS and were dysregulated in one or both HS-Sensitive pB-mutant clones (↑⤯⤯). *Isoprenoid biosynthesis-related genes upregulated by HS confirmed in the pooled HS-Screen.