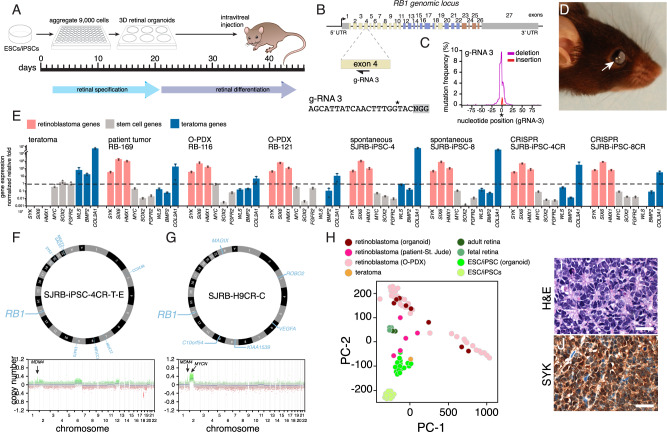
Fig. 3. Retinoblastoma from 3D retinal organoids.
A Schematic drawing of the retinoblastoma workflow. After 45 days of differentiation, retinal organoids are dissociated and injected into the eyes of immunocompromised mice and they are held for 1 year to wait for tumor formation. B Drawing of the RB1 genomic locus with the location of the gRNA targeting exon 4 and the corresponding sequence. C Plot of mutation frequency in a representative iPSC line for gRNA-3 with insertions (red) and deletion (blue) flanking the cut site (*). D Photograph of a mouse with retinoblastoma from a retinal organoid. E Barplot of qRT-PCR for genes found in the retinoblastoma (SYK, SIX3, HMX1), human pluripotent stem cells (MYC, SOX2, FGFR2), and teratomas (WLS, BMP2, COLA1) from one teratoma, one patient tumor (RB-169), two PDX tumors (RB116 and RB121), two spontaneous retinal organoids-derived tumors (SJRB-iPSC-4 and SJRB-iPSC-8), and two CRISPR-modified retinal organoids (SJRB-iPSC-4CR, SJRB-iPSC-8CR). Each dot is the mean of technical duplicates, the bar is the mean and standard deviation between replicates. All data are normalized to GAPDH and plotted relative to H9 ESCs (dashed line). F, G Circos plot of representative organoid-derived retinoblastoma (SJRB-iPSC-4CR-T-E and SJRB-H9CR-T-C) showing somatic mutations acquired in the tumor relative to the iPSC/ESC line. The copy number changes across the genome are shown below each tumor. H Principal component analysis (PCA) of RNA-seq of organoid-derived retinoblastomas, O-PDXs, patient tumors, iPSC/ESCs, and retinal organoids. I, J Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained organoid-derived tumor showing rosettes and IHC for SYK (brown) which is not present in the normal retina but is upregulated in retinoblastoma. Staining was completed on three tumors with similar results. Scale bars: 25 μm.