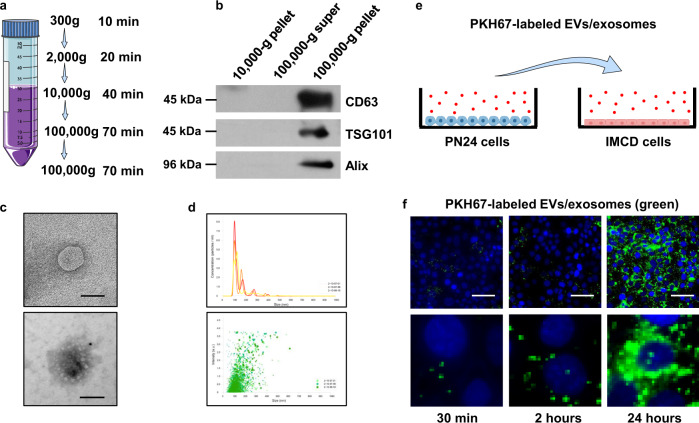
Fig. 1. Pkd1-null renal epithelial cell-derived EVs/exosomes can be taken by recipient cells.
a Protocol of the EVs/exosome isolation and purification from FBS-free media. b Western blot analysis of the 10,000-g pellet, 100,000-g supernatant, and 100,000-g pellet from FBS-free media by sequential centrifugation. The CD63, TSG101, and Alix proteins, markers of exosomes, were abundant in the 100,000-g pellet isolated from FBS-free media. c Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of EVs/exosomes in FBS-free media (top panel) and Immunogold labeled exosomes (bottom panel). Scale bars, 100 nm. d EVs/exosome detection by nanoparticle-tracking analysis (NTA) in FBS-free media. The most often particle diameter is on average of 109.8 nm (top panel), and the distribution histogram showed that the particle diameters were concentrated in the range of 100–110 nm (bottom panel). e Schematic of EVs/exosome uptake experiment. Purified PN24 cell-derived EVs/exosomes were labeled with green fluorescent dye, PKH67, and incubated with mouse IMCD3 cells. f Mouse IMCD3 cells were incubated with PKH67-labeled (green) EVs/exosomes from PN24 cells for 30 min, 2 h, and 24 h, and fixed for immunofluorescence imaging. Scale bars, 100 μm.