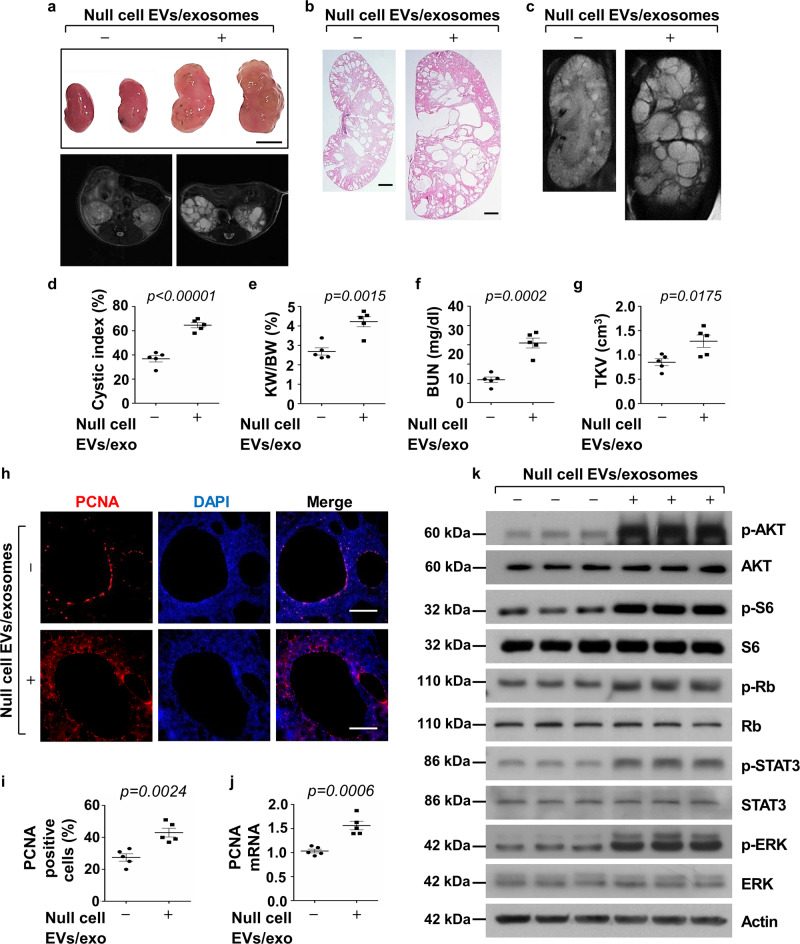
Fig. 4. Treatment with Pkd1-null cell-derived EVs/exosomes promoted cyst growth in vivo.
a Images of kidneys (top panel) and axial MRI (bottom panel) from Pkd1RC/RC mice treated with or without cystic cell-derived EVs/exosomes. Scale bars, 5 mm. b Histological examination of kidneys from Pkd1RC/RC mice treated with or without cystic cell-derived EVs/exosomes. Scale bars, 1 mm. c MRI images from Pkd1RC/RC mice treated with or without cystic cell-derived EVs/exosomes. Scale bars, 1 mm. d Treatment with cystic cell-derived EVs/exosomes increased cyst index in kidneys from Pkd1RC/RC mice treated with cystic exosomes (n = 5) compared to that in control mice treated with PBS (n = 5). Treatment with cystic exosomes increased KW/BW ratios (e) and BUN levels (f) in Pkd1RC/RC mice compared to those in control mice treated with PBS. g Total kidney volume (TKV) was calculated by MRI scan in each group. h Treatment with cystic cell EVs/exosomes increased cyst-lining epithelial and interstitial cell proliferation in kidneys from Pkd1RC/RC mice as detected with PCNA staining. Scale bars, 100 μm. i The percentage of PCNA-positive cells was calculated from an average of 1000 nuclei per mouse kidney section. j qRT-PCR analysis of PCNA mRNA expression in kidneys from Pkd1RC/RC mice treated with cystic cell EVs/exosomes or PBS. k Western blot analysis of the phosphorylation and total proteins of AKT, mTOR, S6, Rb, STAT3 and ERK in kidneys from Pkd1RC/RC mice treated with cystic cell EVs/exosomes or PBS. All statistical data are represented as mean ± SEM, and p values are calculated by unpaired Student’s t-test.