Figure 2: Cross-talk between pulmonary endothelial cells and other cells leads to obliterative pulmonary vascular remodeling and progressive vasoconstriction and thereby PAH.
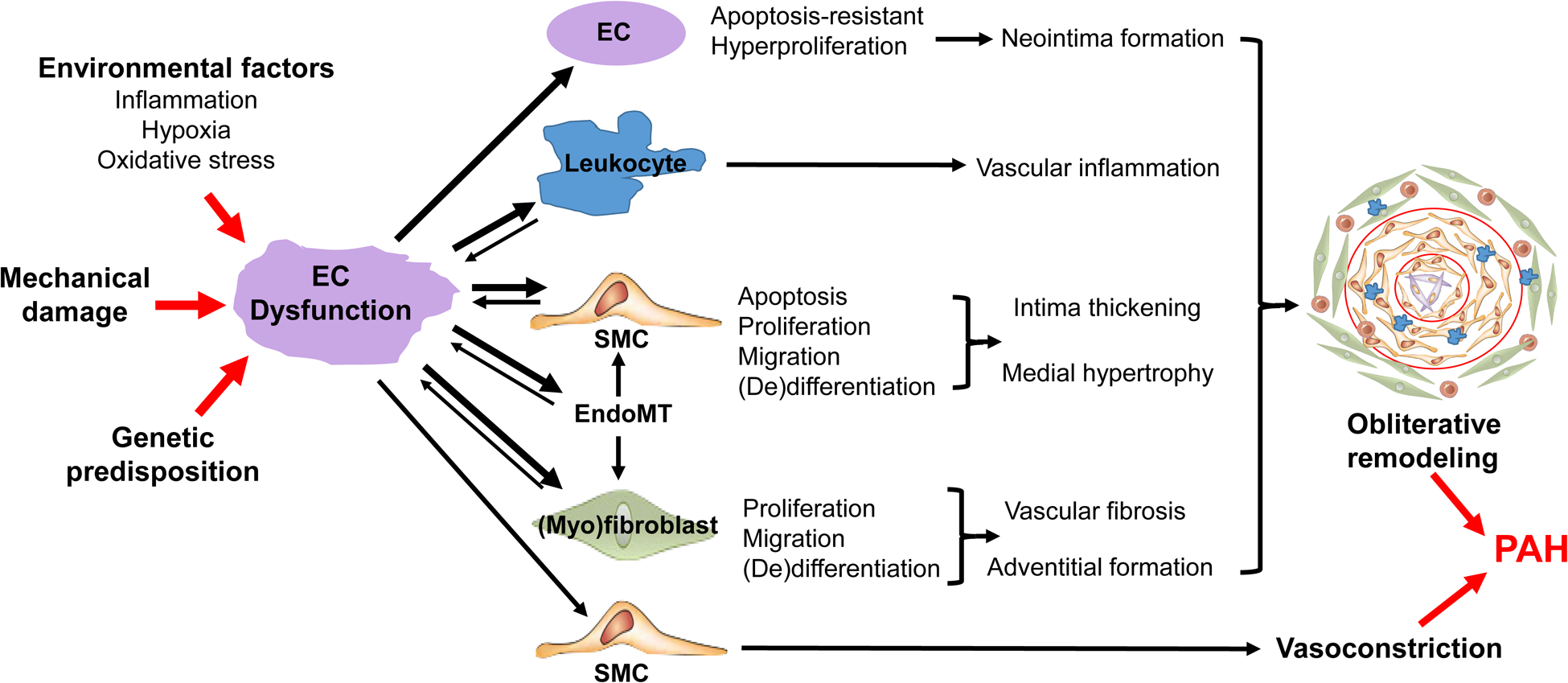
Various environmental factors, mechanical damage, and genetic predisposition converge on pulmonary vascular ECs leading to EC injury and dysfunction which affect EC activation, survival, proliferation, migration, metabolic and epigenetic status resulting in EC-apoptosis-resistant hyperproliferation, EndoMT, and releases of vascular tone modulators, angiocrine factors, cytokine and chemokines which mediate crosstalk between ECs and SMCs, leukocytes, (myo)fibroblasts. Together, EC dysfunction induces obliterative pulmonary vascular remodeling and vasoconstriction resulting in PAH. Thus, targeting altered EC signalings will provide novel effective therapeutic approaches for inhibiting/reversing obliterative vascular remodeling and PAH. Abbreviations: EC, endothelial cell; EndoMT, endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition; PH, pulmonary hypertension; SMC, smooth muscle cell.
