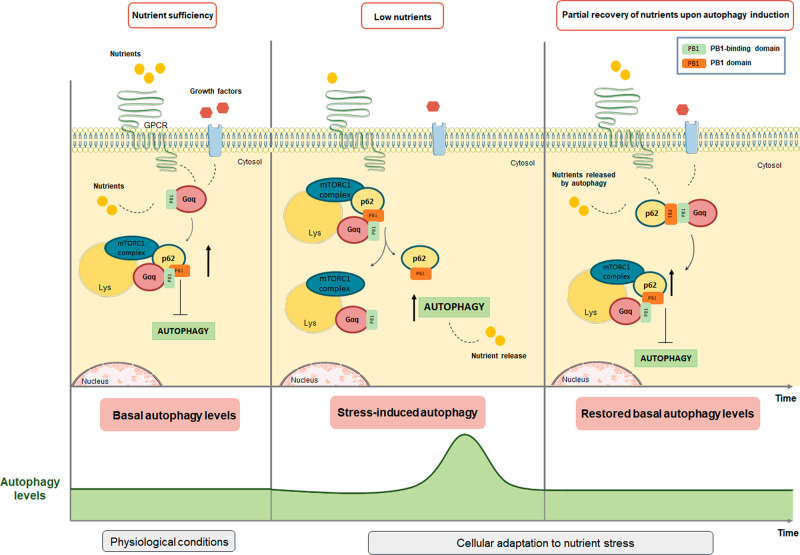
Fig. 8. Proposed scaffolding role of Gαq in the assembly of active mTORC1 complex to control autophagy in response to different types of nutrient stress.
Upper part: In nutrient-sufficiency conditions, the presence of serum, amino acids, or glucose would foster the PB1-like interaction between Gαq and p62, leading to basal mTORC1 stimulation and preservation of homeostatic autophagy levels. Upon starvation, Gαq/p62 dissociation would facilitate the PB1-domain-dependent participation of p62 in the autophagic pathway. The release of internal nutrients during autophagy would in turn facilitate Gαq/p62/mTORC1 complex formation and reactivation in order to terminate autophagy. Lower part: Autophagy levels diagram. In response to starvation, there is a controlled and transient upregulation of autophagy, with a subsequent return to basal levels upon the partial recovery of nutrients.