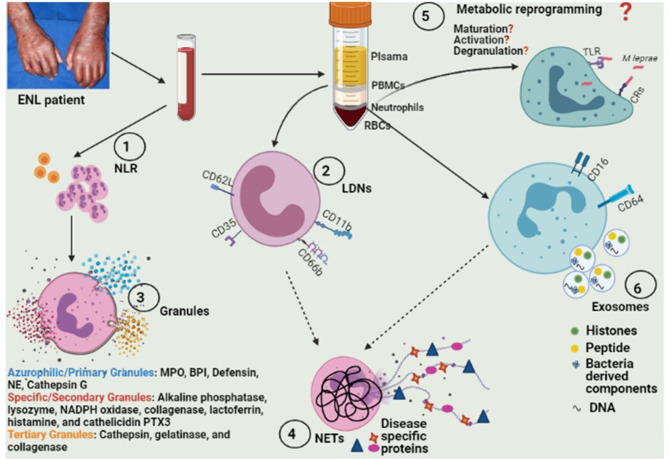
Figure 1.
Model depicting various approaches for exploring different aspects of neutrophil biology for future biomarker discovery. (1) Identification of adequate cut-off values of NLR and their longitudinal evaluations over a prolonged treatment period in larger study cohorts. (2) Elucidation of frequency as well as the expression of various activation surface markers for LDNs (and determination of their clinical significance in ENL pathophysiology). (3) Assessment of differences in neutrophil granules' protein content and their secretion. (4) Evaluation of serum levels of NETs/NETs associated proteins in prospective follow up studies of ENL patients and their correlation with disease activity and also investigation of ENL-specific bioactive proteins loaded on NETs. (5) Exploration of the hypothesis of “M leprae-induced transcriptional-reprogramming” in neutrophils/NETs resulting in alterations in biosynthetic pathways associated with neutrophil maturation, activation, and degranulation. (6) Investigation of functional and diagnostic potential of neutrophil-derived exosomal protein and/or miRNAs. NLR, Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; LDNs, low density neutrophils; ENL, eryhtema nodosum leprosum; NETs, neutrophil extracelluar traps; TLRs, Toll like receptors; CRs, complement receptors; MPO, Myeloperoxidase; BPI, Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein; NE, Neutrophil elastase; PTX3, Pentraxin-3.