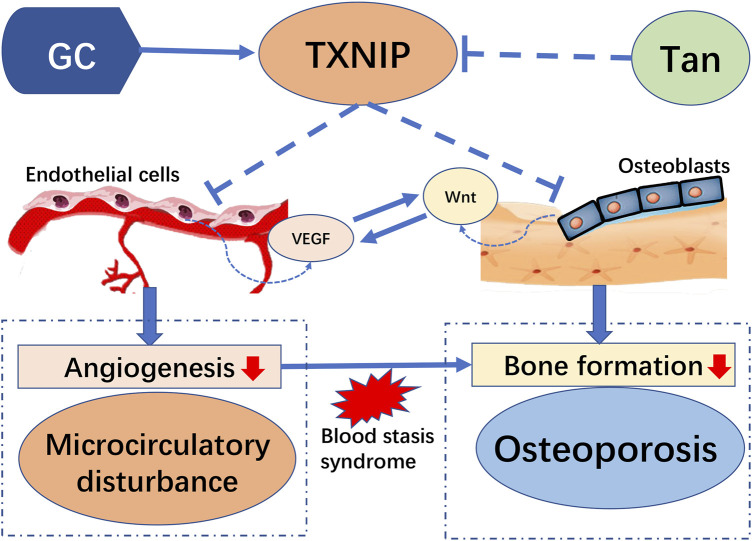
FIGURE 9.
Model of the pathogenesis of GC-induced microcirculation dysfunction and impaired osteogenesis by TXNIP and its intervention of tanshinol: Long-term high-dose glucocorticoid can activate expression of TXNIP proteins. TXNIP down-regulates both VEGF and Wnt signaling pathways in vascular endothelial cells and osteoblasts respectively, contributing to inhibition of angiogenesis, followed by dysfunction of microcirculation in bone vessels, which causes blood stasis and decreased bone formation and eventually induced osteoporosis. However, tanshinol protects rats from GIO involving in the regulation of TXNIP/Wnt/VEGF cascade pathway.