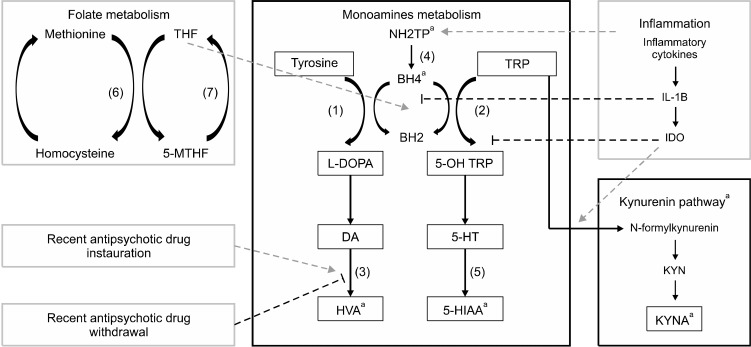
Fig. 3.
Overview of monoamine’s metabolism and the antipsychotic effect on CSF HVA. Antipsychotics influence monoamine’s metabolism by stimulating HVA production after its instauration. Withdrawal provokes a decrease in HVA level. Antipsychotic prescription should be considered as a confounding factor as well as inflammatory processes and folate metabolism when monoamine’s assessment is performed. (1) Tyrosine Hydroxylase; (2) Tryptophan Hydroxylase; (3) Catecholamine-O-Methyl Transferase (COMT) and Monoamine Oxydase (MAO); (4) 6-Pyruvotetrahydropterin Synthase (PTPS) and Sepiapterin Reductase (SR); (5) Aldehyde Deshydrogenase and MAO; (6) Methionine Synthase; (7) Methyltetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR). NH2TP, dihydroneopterin triphosphate; BH2, Dihydrobiopterin; BH4, Tetrahydrobiopterin; TRP, Tryptophan; DOPA, Dopamin; NA, Noradrenaline; 5-HT, serotonin; MHPG, 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol; HVA, Homovanillic acid; 5-HIAA, 5-hydroxyindolamine acetic acid. aCan be measured in CSF.